CHINESE MONEY
The Chinese are a curious people, and have strange inverted ways of doing things. It is said that they use a saw with an upward pressure instead of a downward one, that they plane a deal board by pulling the tool toward them instead of pushing it, and that in building a house they first construct the roof and, having raised that into position, proceed to work downwards. In money the currency of the country consists of taels of fluctuating value. The tael became thinner and thinner until `2,000` of them piled together made less than three inches in height. The common cash consists of brass coins of varying thicknesses, with a round, square, or triangular hole in the centre, as in our illustration. 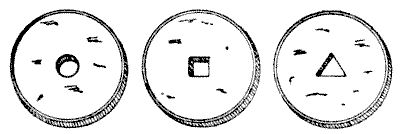 These are strung on wires like buttons. Supposing that eleven coins with round holes are worth fifteen ching-changs, that eleven with square holes are worth sixteen ching-changs, and that eleven with triangular holes are worth seventeen ching-changs, how can a Chinaman give me change for half a crown, using no coins other than the three mentioned? A ching-chang is worth exactly twopence and four-fifteenths of a ching-chang.
These are strung on wires like buttons. Supposing that eleven coins with round holes are worth fifteen ching-changs, that eleven with square holes are worth sixteen ching-changs, and that eleven with triangular holes are worth seventeen ching-changs, how can a Chinaman give me change for half a crown, using no coins other than the three mentioned? A ching-chang is worth exactly twopence and four-fifteenths of a ching-chang.
 These are strung on wires like buttons. Supposing that eleven coins with round holes are worth fifteen ching-changs, that eleven with square holes are worth sixteen ching-changs, and that eleven with triangular holes are worth seventeen ching-changs, how can a Chinaman give me change for half a crown, using no coins other than the three mentioned? A ching-chang is worth exactly twopence and four-fifteenths of a ching-chang.
These are strung on wires like buttons. Supposing that eleven coins with round holes are worth fifteen ching-changs, that eleven with square holes are worth sixteen ching-changs, and that eleven with triangular holes are worth seventeen ching-changs, how can a Chinaman give me change for half a crown, using no coins other than the three mentioned? A ching-chang is worth exactly twopence and four-fifteenths of a ching-chang.
Sources:
- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 25
There are no comments yet.