Geometry, Solid Geometry / Geometry in Space, Polyhedra, Regular Polyhedra
Regular Polyhedra, also known as Platonic solids, are polyhedra where all faces are identical regular polygons, and the same number of faces meet at each vertex. Questions explore their unique properties, symmetries, nets, and calculations related to their dimensions.
-
Question
A regular polygon with 4k sides is divided into parallelograms. Prove that among these parallelograms there are at least k rectangles. Find the sum of the areas of all the rectangles.
Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Solid Geometry / Geometry in Space -> Polyhedra -> Regular Polyhedra -
THE PENTAGON AND SQUARE
I wonder how many of my readers, amongst those who have not given any close attention to the elements of geometry, could draw a regular pentagon, or five-sided figure, if they suddenly required to do so. A regular hexagon, or six-sided figure, is easy enough, for everybody knows that all you have to do is to describe a circle and then, taking the radius as the length of one of the sides, mark off the six points round the circumference. But a pentagon is quite another matter. So, as my puzzle has to do with the cutting up of a regular pentagon, it will perhaps be well if I first show my less experienced readers how this figure is to be correctly drawn. Describe a circle and draw the two lines H B and D G, in the diagram, through the centre at right angles. Now find the point A, midway between C and B. Next place the point of your compasses at A and with the distance A D describe the arc cutting H B at E. Then place the point of your compasses at D and with the distance D E describe the arc cutting the circumference at F. Now, D F is one of the sides of your pentagon, and you have simply to mark off the other sides round the circle. Quite simple when you know how, but otherwise somewhat of a poser.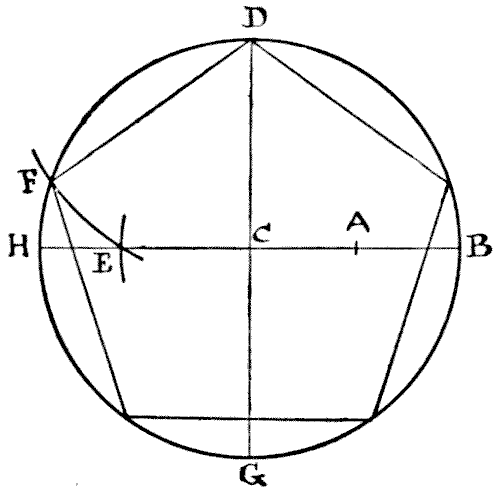 Having formed your pentagon, the puzzle is to cut it into the fewest possible pieces that will fit together and form a perfect square.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry Geometry -> Area Calculation Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Geometry -> Solid Geometry / Geometry in Space -> Polyhedra -> Regular Polyhedra
Having formed your pentagon, the puzzle is to cut it into the fewest possible pieces that will fit together and form a perfect square.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry Geometry -> Area Calculation Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Geometry -> Solid Geometry / Geometry in Space -> Polyhedra -> Regular Polyhedra- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 155
-
THE FLY ON THE OCTAHEDRON
"Look here," said the professor to his colleague, "I have been watching that fly on the octahedron, and it confines its walks entirely to the edges. What can be its reason for avoiding the sides?"
"Perhaps it is trying to solve some route problem," suggested the other. "Supposing it to start from the top point, how many different routes are there by which it may walk over all the edges, without ever going twice along the same edge in any route?"
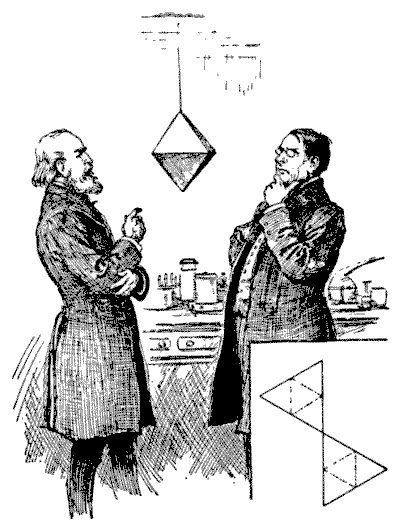
The problem was a harder one than they expected, and after working at it during leisure moments for several days their results did not agree—in fact, they were both wrong. If the reader is surprised at their failure, let him attempt the little puzzle himself. I will just explain that the octahedron is one of the five regular, or Platonic, bodies, and is contained under eight equal and equilateral triangles. If you cut out the two pieces of cardboard of the shape shown in the margin of the illustration, cut half through along the dotted lines and then bend them and put them together, you will have a perfect octahedron. In any route over all the edges it will be found that the fly must end at the point of departure at the top.
Sources:Topics:Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry Combinatorics -> Graph Theory Geometry -> Solid Geometry / Geometry in Space -> Polyhedra -> Regular Polyhedra- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 245
-
THE ICOSAHEDRON PUZZLE
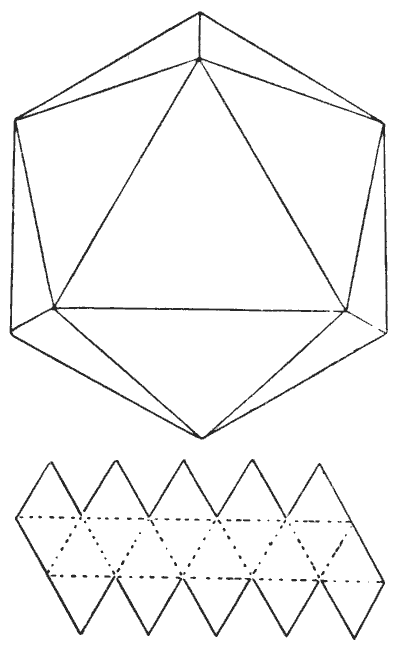
The icosahedron is another of the five regular, or Platonic, bodies having all their sides, angles, and planes similar and equal. It is bounded by twenty similar equilateral triangles. If you cut out a piece of cardboard of the form shown in the smaller diagram, and cut half through along the dotted lines, it will fold up and form a perfect icosahedron.
Now, a Platonic body does not mean a heavenly body; but it will suit the purpose of our puzzle if we suppose there to be a habitable planet of this shape. We will also suppose that, owing to a superfluity of water, the only dry land is along the edges, and that the inhabitants have no knowledge of navigation. If every one of those edges is `10,000` miles long and a solitary traveller is placed at the North Pole (the highest point shown), how far will he have to travel before he will have visited every habitable part of the planet—that is, have traversed every one of the edges?
 Sources:Topics:Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry Combinatorics -> Graph Theory Geometry -> Solid Geometry / Geometry in Space -> Polyhedra -> Regular Polyhedra
Sources:Topics:Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry Combinatorics -> Graph Theory Geometry -> Solid Geometry / Geometry in Space -> Polyhedra -> Regular Polyhedra- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 246