Arithmetic, Fractions
Fractions represent parts of a whole or ratios between numbers. This topic covers understanding, comparing, simplifying, and performing arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division) with fractions and mixed numbers. Questions often involve practical applications.
-
THE FOUR SEVENS
Sources: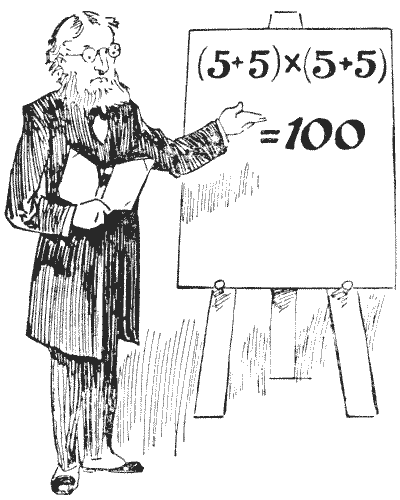 In the illustration Professor Rackbrane is seen demonstrating one of the little posers with which he is accustomed to entertain his class. He believes that by taking his pupils off the beaten tracks he is the better able to secure their attention, and to induce original and ingenious methods of thought. He has, it will be seen, just shown how four `5`'s may be written with simple arithmetical signs so as to represent `100`. Every juvenile reader will see at a glance that his example is quite correct. Now, what he wants you to do is this: Arrange four `7`'s (neither more nor less) with arithmetical signs so that they shall represent `100`. If he had said we were to use four `9`'s we might at once have written `99 9/9`, but the four `7`'s call for rather more ingenuity. Can you discover the little trick?
In the illustration Professor Rackbrane is seen demonstrating one of the little posers with which he is accustomed to entertain his class. He believes that by taking his pupils off the beaten tracks he is the better able to secure their attention, and to induce original and ingenious methods of thought. He has, it will be seen, just shown how four `5`'s may be written with simple arithmetical signs so as to represent `100`. Every juvenile reader will see at a glance that his example is quite correct. Now, what he wants you to do is this: Arrange four `7`'s (neither more nor less) with arithmetical signs so that they shall represent `100`. If he had said we were to use four `9`'s we might at once have written `99 9/9`, but the four `7`'s call for rather more ingenuity. Can you discover the little trick?- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 95
-
THE GREAT SCRAMBLE
After dinner, the five boys of a household happened to find a parcel of sugar-plums. It was quite unexpected loot, and an exciting scramble ensued, the full details of which I will recount with accuracy, as it forms an interesting puzzle.
You see, Andrew managed to get possession of just two-thirds of the parcel of sugar-plums. Bob at once grabbed three-eighths of these, and Charlie managed to seize three-tenths also. Then young David dashed upon the scene, and captured all that Andrew had left, except one-seventh, which Edgar artfully secured for himself by a cunning trick. Now the fun began in real earnest, for Andrew and Charlie jointly set upon Bob, who stumbled against the fender and dropped half of all that he had, which were equally picked up by David and Edgar, who had crawled under a table and were waiting. Next, Bob sprang on Charlie from a chair, and upset all the latter's collection on to the floor. Of this prize Andrew got just a quarter, Bob gathered up one-third, David got two-sevenths, while Charlie and Edgar divided equally what was left of that stock.

They were just thinking the fray was over when David suddenly struck out in two directions at once, upsetting three-quarters of what Bob and Andrew had last acquired. The two latter, with the greatest difficulty, recovered five-eighths of it in equal shares, but the three others each carried off one-fifth of the same. Every sugar-plum was now accounted for, and they called a truce, and divided equally amongst them the remainder of the parcel. What is the smallest number of sugar-plums there could have been at the start, and what proportion did each boy obtain?
Sources:- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 109
-
A PUZZLING LEGACY
A man left a hundred acres of land to be divided among his three sons—Alfred, Benjamin, and Charles—in the proportion of one-third, one-fourth, and one-fifth respectively. But Charles died. How was the land to be divided fairly between Alfred and Benjamin? Sources:- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 112
-
A LEGAL DIFFICULTY
"A client of mine," said a lawyer, "was on the point of death when his wife was about to present him with a child. I drew up his will, in which he settled two-thirds of his estate upon his son (if it should happen to be a boy) and one-third on the mother. But if the child should be a girl, then two-thirds of the estate should go to the mother and one-third to the daughter. As a matter of fact, after his death twins were born—a boy and a girl. A very nice point then arose. How was the estate to be equitably divided among the three in the closest possible accordance with the spirit of the dead man's will?" Sources:- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 123
-
THE SCULPTOR'S PROBLEM
An ancient sculptor was commissioned to supply two statues, each on a cubical pedestal. It is with these pedestals that we are concerned. They were of unequal sizes, as will be seen in the illustration, and when the time arrived for payment a dispute arose as to whether the agreement was based on lineal or cubical measurement. But as soon as they came to measure the two pedestals the matter was at once settled, because, curiously enough, the number of lineal feet was exactly the same as the number of cubical feet. The puzzle is to find the dimensions for two pedestals having this peculiarity, in the smallest possible figures. You see, if the two pedestals, for example, measure respectively `3` ft. and `1` ft. on every side, then the lineal measurement would be `4` ft. and the cubical contents `28` ft., which are not the same, so these measurements will not do.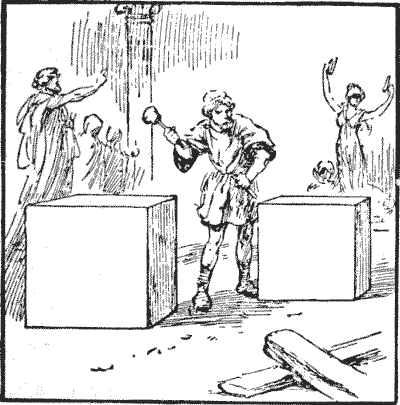 Sources:Topics:Number Theory Geometry -> Solid Geometry / Geometry in Space Arithmetic -> Fractions Algebra -> Equations -> Diophantine Equations
Sources:Topics:Number Theory Geometry -> Solid Geometry / Geometry in Space Arithmetic -> Fractions Algebra -> Equations -> Diophantine Equations- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 130
-
THE DOCTOR'S QUERY
"A curious little point occurred to me in my dispensary this morning," said a doctor. "I had a bottle containing ten ounces of spirits of wine, and another bottle containing ten ounces of water. I poured a quarter of an ounce of spirits into the water and shook them up together. The mixture was then clearly forty to one. Then I poured back a quarter-ounce of the mixture, so that the two bottles should again each contain the same quantity of fluid. What proportion of spirits to water did the spirits of wine bottle then contain?" Sources:- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 363
-
WINE AND WATER
Mr. Goodfellow has adopted a capital idea of late. When he gives a little dinner party and the time arrives to smoke, after the departure of the ladies, he sometimes finds that the conversation is apt to become too political, too personal, too slow, or too scandalous. Then he always manages to introduce to the company some new poser that he has secreted up his sleeve for the occasion. This invariably results in no end of interesting discussion and debate, and puts everybody in a good humour.
Here is a little puzzle that he propounded the other night, and it is extraordinary how the company differed in their answers. He filled a wine-glass half full of wine, and another glass twice the size one-third full of wine. Then he filled up each glass with water and emptied the contents of both into a tumbler. "Now," he said, "what part of the mixture is wine and what part water?" Can you give the correct answer?
Sources:- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 367
-
THE BARRELS OF HONEY

Once upon a time there was an aged merchant of Bagdad who was much respected by all who knew him. He had three sons, and it was a rule of his life to treat them all exactly alike. Whenever one received a present, the other two were each given one of equal value. One day this worthy man fell sick and died, bequeathing all his possessions to his three sons in equal shares.
The only difficulty that arose was over the stock of honey. There were exactly twenty-one barrels. The old man had left instructions that not only should every son receive an equal quantity of honey, but should receive exactly the same number of barrels, and that no honey should be transferred from barrel to barrel on account of the waste involved. Now, as seven of these barrels were full of honey, seven were half-full, and seven were empty, this was found to be quite a puzzle, especially as each brother objected to taking more than four barrels of, the same description—full, half-full, or empty. Can you show how they succeeded in making a correct division of the property?
Sources:Topics:Algebra -> Word Problems Arithmetic -> Fractions Combinatorics -> Case Analysis / Checking Cases -> Processes / Procedures Number Theory -> Division- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 372
-
THE MOTOR-CAR RACE
Sometimes a quite simple statement of fact, if worded in an unfamiliar manner, will cause considerable perplexity. Here is an example, and it will doubtless puzzle some of my more youthful readers just a little. I happened to be at a motor-car race at Brooklands, when one spectator said to another, while a number of cars were whirling round and round the circular track:—
"There's Gogglesmith—that man in the white car!"
"Yes, I see," was the reply; "but how many cars are running in this race?"
Then came this curious rejoinder:—
"One-third of the cars in front of Gogglesmith added to three-quarters of those behind him will give you the answer."
Now, can you tell how many cars were running in the race?
Sources:- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 391
-
PHEASANT-SHOOTING
A Cockney friend, who is very apt to draw the long bow, and is evidently less of a sportsman than he pretends to be, relates to me the following not very credible yarn:—
"I've just been pheasant-shooting with my friend the duke. We had splendid sport, and I made some wonderful shots. What do you think of this, for instance? Perhaps you can twist it into a puzzle. The duke and I were crossing a field when suddenly twenty-four pheasants rose on the wing right in front of us. I fired, and two-thirds of them dropped dead at my feet. Then the duke had a shot at what were left, and brought down three-twenty-fourths of them, wounded in the wing. Now, out of those twenty-four birds, how many still remained?"
It seems a simple enough question, but can the reader give a correct answer?
Sources:- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 427