Geometry, Plane Geometry, Symmetry
Symmetry in geometry refers to a shape or object remaining unchanged under certain transformations like reflection (line symmetry) or rotation (rotational symmetry). Questions involve identifying types of symmetry, lines of symmetry, and centers/orders of rotation for various figures.
-
Question
Divide the given shape into four congruent parts:
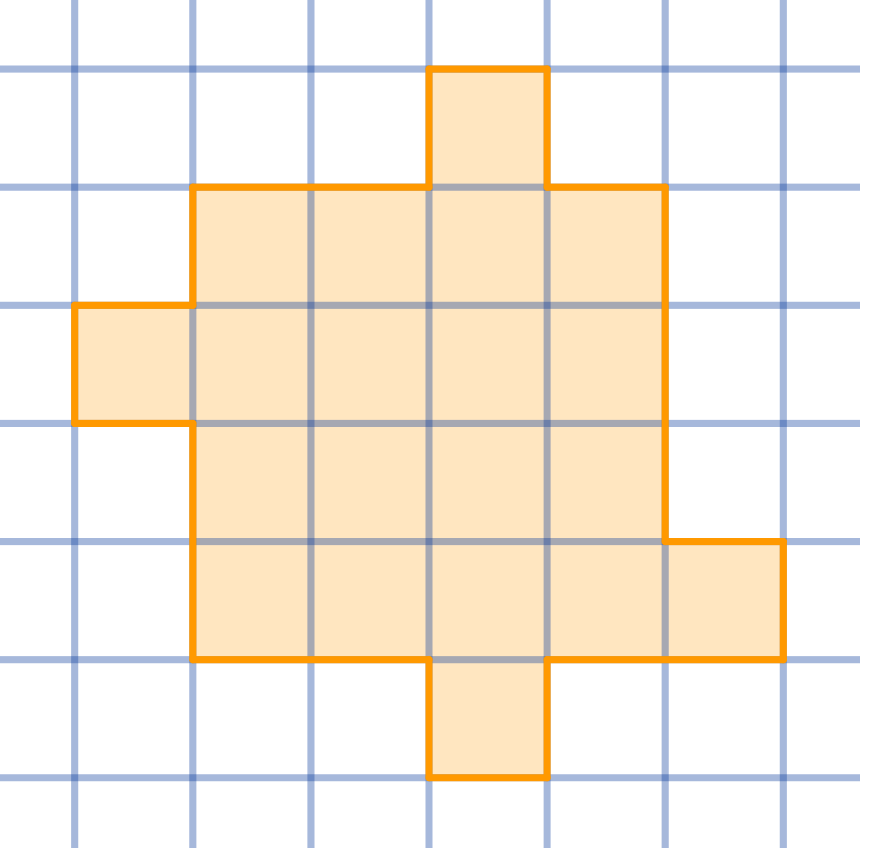 Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries)
Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries) -
Question
Dissect the given shape into four congruent parts:
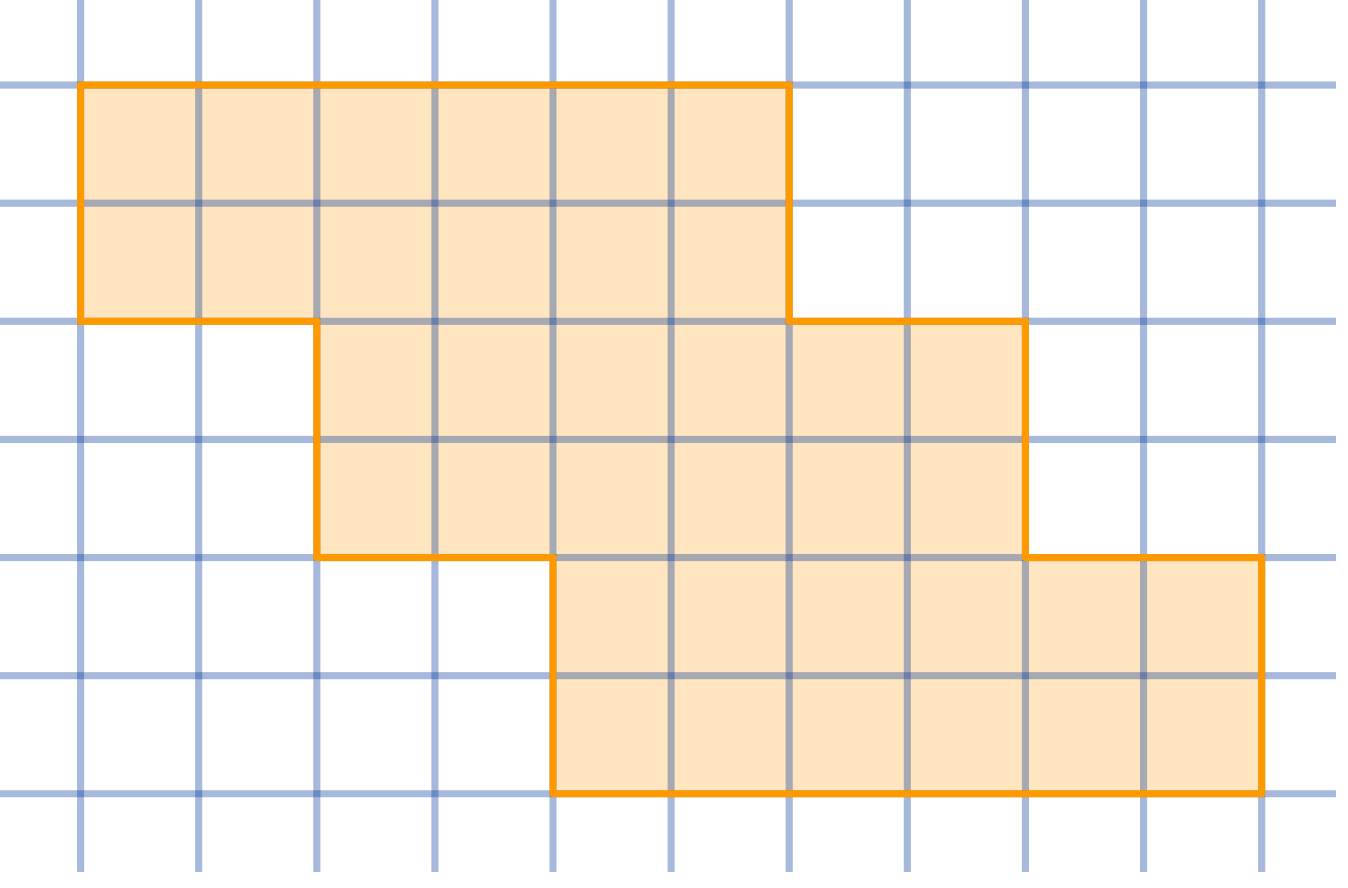 Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries)
Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries) -
Question
Dissect the given shape into four congruent parts:
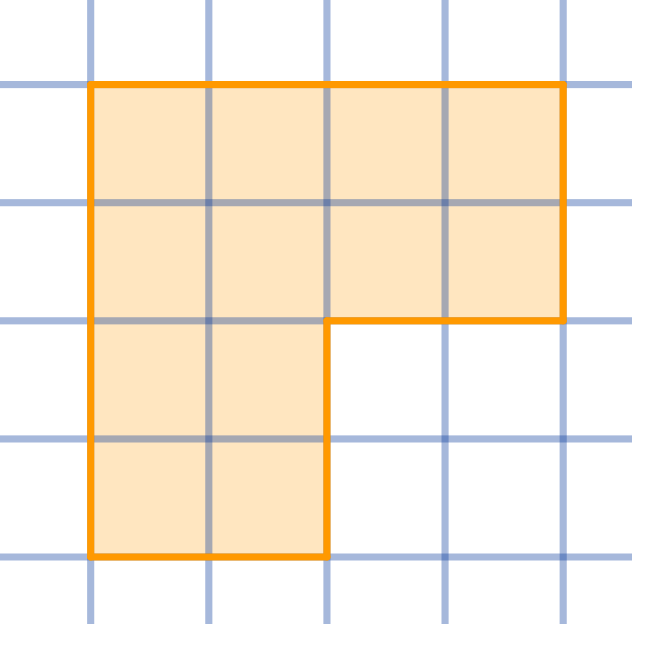 Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries)
Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries) -
Question
In the figure, a semicircle is shown with three circles inscribed within it: the large circle, tangent to the diameter of the semicircle at its center, and two smaller circles on the sides, symmetrically arranged. Which area is larger: the shaded area or the unshaded area?
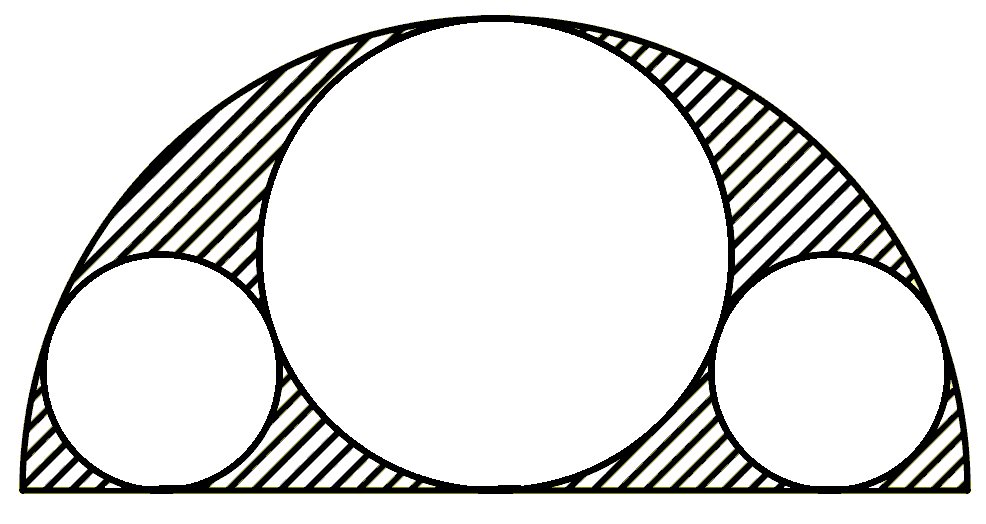 Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Circles Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry
Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Circles Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry -
Quarter Yin-Yang
The shape in the drawing is constructed as follows: Divide the diameter of a semicircle into two equal parts, and construct two additional semicircles on them as diameters: one inwards, and one outwards.
Divide the shape into two congruent parts.
Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Circles Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems -
Question
It is known that all the angles of the given shape are right angles. Cut the shape into two polygons of equal area. You are only allowed to use an unmarked ruler.
-
Gray Area
In the figure is a rectangle composed of 5 squares of size `2 times 2 ` and a line that intersects it diagonally.
Find the area of the shaded region.
Sources: -
Question
The numbers `1,2,3,4,5` are written at the vertices of a regular pentagon, with each number at exactly one vertex. A trio of vertices is called successful if it forms an isosceles triangle, where the number at its apex is greater than the numbers at the other two vertices, or where the number at its apex is smaller than the numbers at the other two vertices.
Find the maximum number of successful trios that can exist.
-
Dissect into four parts
Geometric shapes are called congruent if they coincide when superimposed. Cut the following shape into four congruent parts:
Sources: -
Cut a Boat in Half
Geometric shapes are called congruent if they coincide when placed on top of each other. Cut the shape into two congruent parts
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems




