Proof and Example
This category emphasizes the core mathematical activities of constructing rigorous arguments (proofs) to establish general truths, and using specific instances (examples) to illustrate concepts, test conjectures, or find counterexamples. Questions may ask for either or both.
Constructing an Example / Counterexample Proof by Contradiction-
Question
Prove that for every prime number `p>3 ` the following holds: `p^2-1` is divisible by `6`.
-
Question
Prove that any real number can be written as the sum of 9 numbers, each of which is composed only of the digits 0 and 7.
Sources: -
Question
Prove that the product of two consecutive numbers is always even.
-
Question
Given a real number `a` such that `a+1/a` is an integer. Prove that `a^2+1/a^2` is also an integer.
-
Question
Given a real number `a` such that `a+1/a` is an integer. Prove that `a^n+1/a^n` is also an integer for every natural number `n`.
-
Question
Two congruent triangles form a Star of David as depicted in the drawing. Prove that the shaded area is equal to the hatched area.
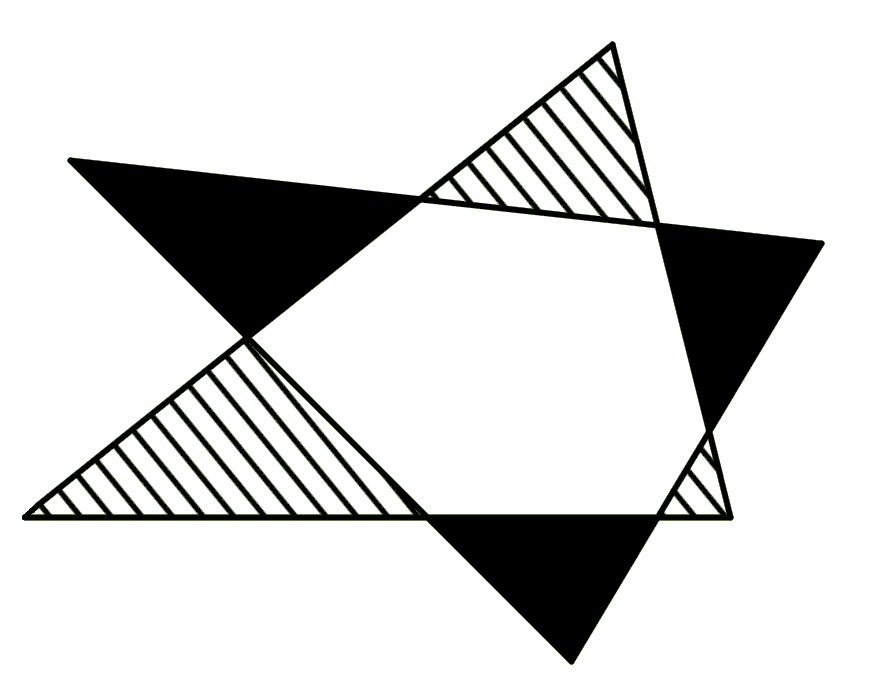 Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Proof and Example Set Theory Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Triangles -> Triangle Congruence
Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Proof and Example Set Theory Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Triangles -> Triangle Congruence -
Question
Can you cut the shape on the left into six shapes like the shape on the right?
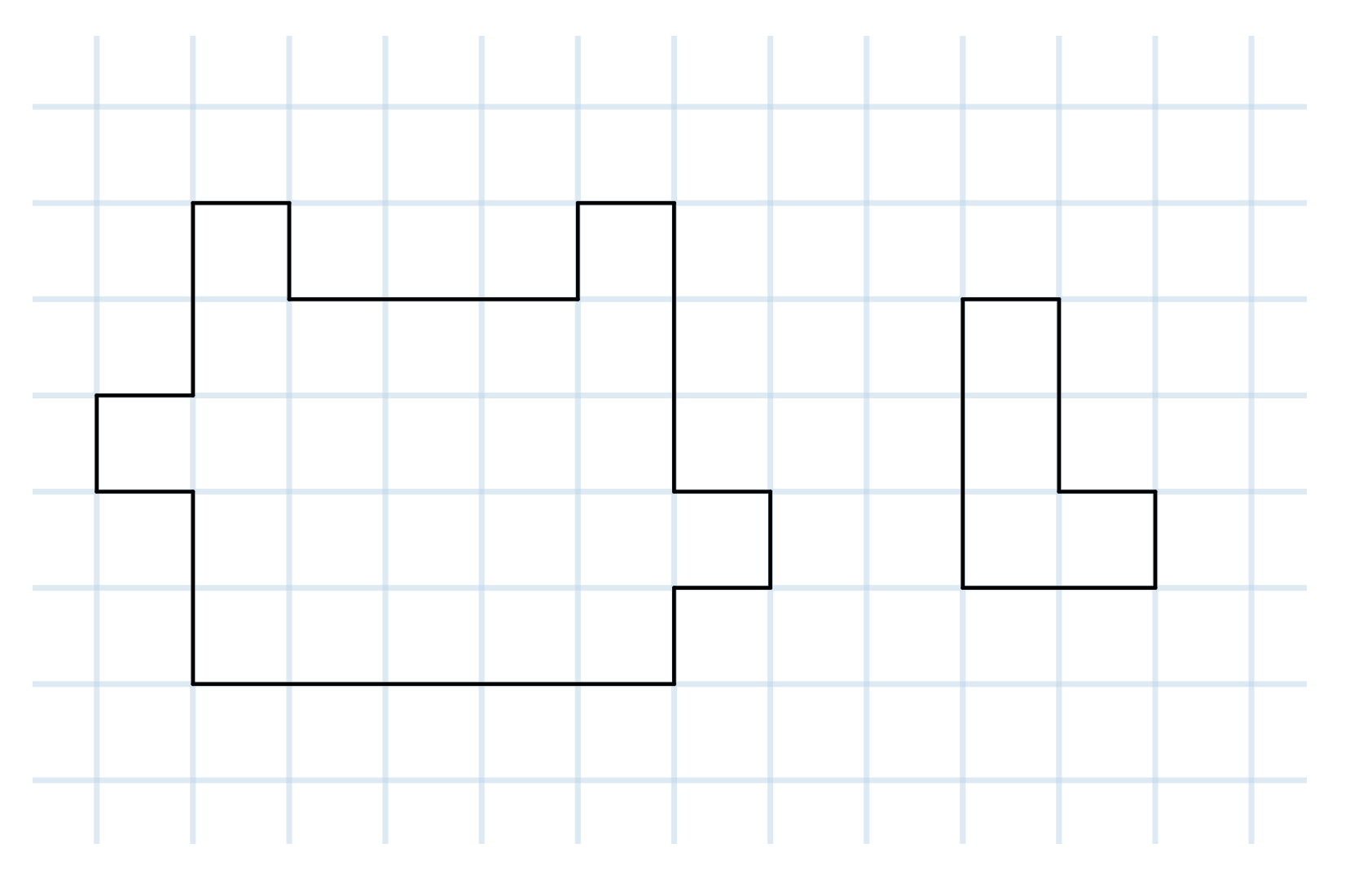
-
Question
Prove that the sum of two consecutive numbers is always odd.
-
Question
Given two numbers such that one is obtained from the other by changing the order of its digits. Prove that their difference is divisible by `9`.
-
Question
Given a natural number `n` that is three times greater than the sum of its digits. Prove that `n` is divisible by `27`.