Logic, Reasoning / Logic
This category emphasizes general logical reasoning skills, often applied to puzzles or scenarios not strictly formal. It involves deduction, inference, identifying patterns, and drawing sound conclusions from given information. It overlaps with formal logic but can be broader.
Paradoxes-
Question
There are `30` students in a class. During a test, Pinchas made `13` mistakes, and the rest made fewer mistakes. Prove that there are three students who made the same number of mistakes.
-
Who Broke the Glass?
One of the following four students: Avi, Benny, Gili, and Danny – broke a glass. The principal asks them who did it. Here are the answers she received:
Avi: I know for certain that whoever broke the glass, it was not me or Benny.
Benny: I know for certain that whoever broke the glass, it was not me or Danny.
Gili: I know for certain that whoever broke the glass, it was not me or Benny.
Danny: I know for certain that whoever broke the glass, it was not me or Avi.
It is known that only one of them broke the glass, and it is also known that three of the students told the truth, and one lied. So who broke the glass?
-
Question
This year, Yossi participated in the Mathematics Olympiad for the first time. Before the Olympiad, a survey was conducted in which each participant was asked what place they thought they would achieve. Yossi answered that he would probably be in last place. After the competition itself, it turned out that every participant, except for Yossi, achieved a worse place than they answered in the survey. What place did Yossi take in the Olympiad?
-
Question
A two-digit number is written on the board. Avi claims that the units digit of the number is twice the tens digit. Beni claims that the number is divisible by `9`. Gal claims that the number is divisible by `4`. Dani claims that the number is divisible by `27`. It is known that one of them is wrong, and the rest are correct. What number is written on the board?
Topics:Number Theory -> Modular Arithmetic / Remainder Arithmetic -> Divisibility Rules -> Divisibility Rules by 2, 4, and 8 Number Theory -> Modular Arithmetic / Remainder Arithmetic -> Divisibility Rules -> Divisibility Rules by 3 and 9 Algebra -> Word Problems Logic -> Reasoning / Logic Combinatorics -> Case Analysis / Checking Cases -> Processes / Procedures -
Question
How many triangles are there in the image?
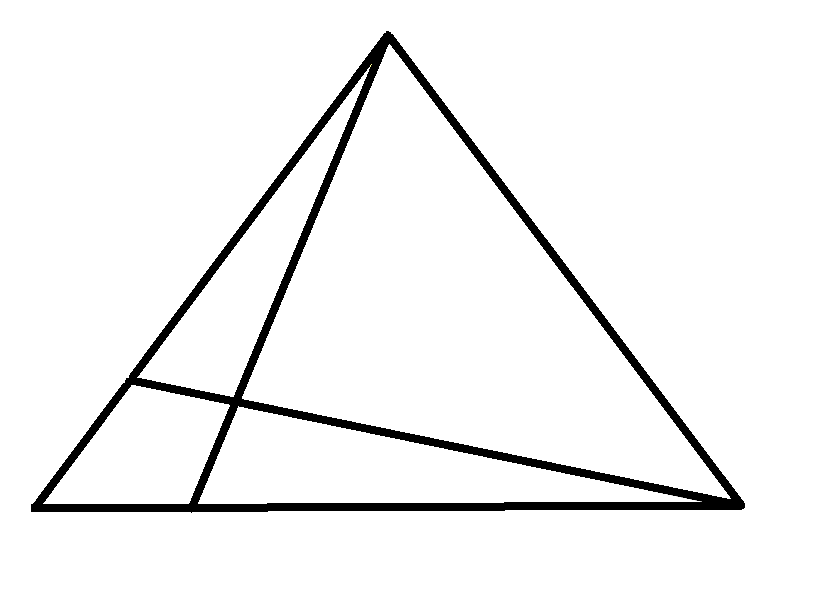 Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Triangles Logic -> Reasoning / Logic Combinatorics -> Case Analysis / Checking Cases -> Processes / Procedures
Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Triangles Logic -> Reasoning / Logic Combinatorics -> Case Analysis / Checking Cases -> Processes / Procedures -
9 Coins
Given `9` coins that look identical. One of the coins is counterfeit, and its weight is less than the weight of a regular coin. How to find the counterfeit coin using two weighings on a balance scale without weights?
-
26 Coins
Given `26` coins that look identical. One of the coins is counterfeit, and it weighs less than a regular coin. How can you find the counterfeit coin using three weighings on a balance scale without weights?
-
80 Coins
Given `80` coins that look identical. One of the coins is counterfeit and weighs less than a regular coin. How can you find the counterfeit coin using four weighings on a balance scale without weights?
-
Question
By how much is the sum of all even numbers not exceeding `100` greater than the sum of all odd numbers not exceeding `100`?
-
Question
A. You have a large jug of 12 liters of olive oil and two empty smaller vessels, one of 5 liters and one of 8 liters. Can you divide the oil you have into two equal parts, if you only have these vessels and no additional measuring tools?
B. The same question, but instead of the 5-liter vessel, you have a 4-liter vessel.
Topics:Number Theory -> Modular Arithmetic / Remainder Arithmetic -> Divisibility Rules Combinatorics -> Invariants Logic -> Reasoning / Logic Number Theory -> Division -> Parity (Even/Odd) Proof and Example -> Constructing an Example / Counterexample Number Theory -> Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM) -> Euclidean Algorithm Combinatorics -> Case Analysis / Checking Cases -> Processes / Procedures Proof and Example -> Proof by Contradiction