Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney
-
Question 171 - THE BANNER PUZZLE
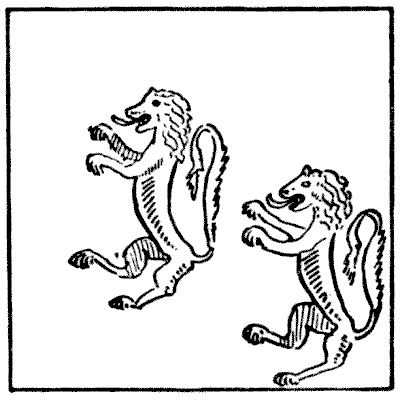 A Lady had a square piece of bunting with two lions on it, of which the illustration is an exactly reproduced reduction. She wished to cut the stuff into pieces that would fit together and form two square banners with a lion on each banner. She discovered that this could be done in as few as four pieces. How did she manage it? Of course, to cut the British Lion would be an unpardonable offence, so you must be careful that no cut passes through any portion of either of them. Ladies are informed that no allowance whatever has to be made for "turnings," and no part of the material may be wasted. It is quite a simple little dissection puzzle if rightly attacked. Remember that the banners have to be perfect squares, though they need not be both of the same size.
A Lady had a square piece of bunting with two lions on it, of which the illustration is an exactly reproduced reduction. She wished to cut the stuff into pieces that would fit together and form two square banners with a lion on each banner. She discovered that this could be done in as few as four pieces. How did she manage it? Of course, to cut the British Lion would be an unpardonable offence, so you must be careful that no cut passes through any portion of either of them. Ladies are informed that no allowance whatever has to be made for "turnings," and no part of the material may be wasted. It is quite a simple little dissection puzzle if rightly attacked. Remember that the banners have to be perfect squares, though they need not be both of the same size.
-
Question 172 - MRS. SMILEY'S CHRISTMAS PRESENT
Mrs. Smiley's expression of pleasure was sincere when her six granddaughters sent to her, as a Christmas present, a very pretty patchwork quilt, which they had made with their own hands. It was constructed of square pieces of silk material, all of one size, and as they made a large quilt with fourteen of these little squares on each side, it is obvious that just `196` pieces had been stitched into it. Now, the six granddaughters each contributed a part of the work in the form of a perfect square (all six portions being different in size), but in order to join them up to form the square quilt it was necessary that the work of one girl should be unpicked into three separate pieces. Can you show how the joins might have been made? Of course, no portion can be turned over.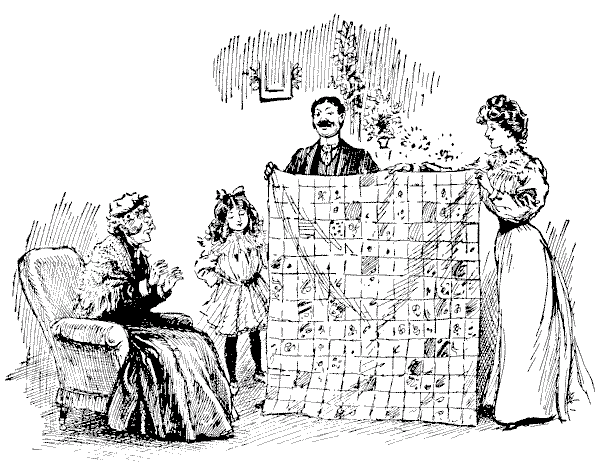
-
Question 173 - MRS. PERKINS'S QUILT
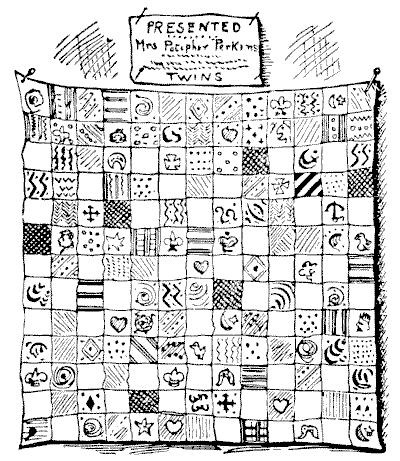 It will be seen that in this case the square patchwork quilt is built up of `169` pieces. The puzzle is to find the smallest possible number of square portions of which the quilt could be composed and show how they might be joined together. Or, to put it the reverse way, divide the quilt into as few square portions as possible by merely cutting the stitches.
It will be seen that in this case the square patchwork quilt is built up of `169` pieces. The puzzle is to find the smallest possible number of square portions of which the quilt could be composed and show how they might be joined together. Or, to put it the reverse way, divide the quilt into as few square portions as possible by merely cutting the stitches.
-
Question 174 - THE SQUARES OF BROCADE
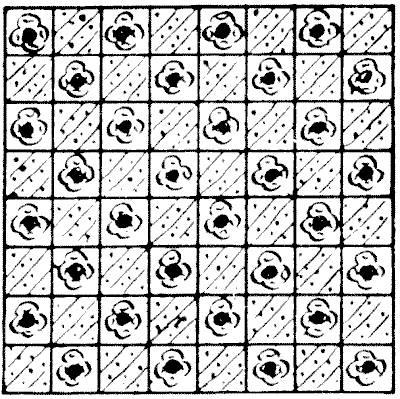
I happened to be paying a call at the house of a lady, when I took up from a table two lovely squares of brocade. They were beautiful specimens of Eastern workmanship—both of the same design, a delicate chequered pattern
."Are they not exquisite?" said my friend. "They were brought to me by a cousin who has just returned from India. Now, I want you to give me a little assistance. You see, I have decided to join them together so as to make one large square cushion-cover. How should I do this so as to mutilate the material as little as possible? Of course I propose to make my cuts only along the lines that divide the little chequers."
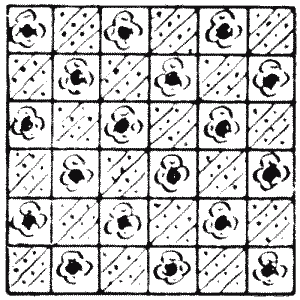
I cut the two squares in the manner desired into four pieces that would fit together and form another larger square, taking care that the pattern should match properly, and when I had finished I noticed that two of the pieces were of exactly the same area; that is, each of the two contained the same number of chequers. Can you show how the cuts were made in accordance with these conditions?
-
Question 175 - ANOTHER PATCHWORK PUZZLE
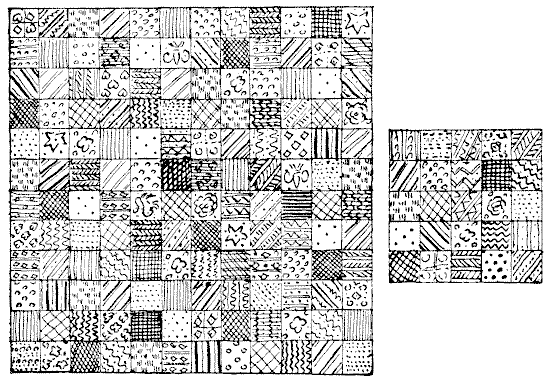 A lady was presented, by two of her girl friends, with the pretty pieces of silk patchwork shown in our illustration. It will be seen that both pieces are made up of squares all of the same size—one 12x12 and the other 5x5. She proposes to join them together and make one square patchwork quilt, 13x13, but, of course, she will not cut any of the material—merely cut the stitches where necessary and join together again. What perplexes her is this. A friend assures her that there need be no more than four pieces in all to join up for the new quilt. Could you show her how this little needlework puzzle is to be solved in so few pieces?
A lady was presented, by two of her girl friends, with the pretty pieces of silk patchwork shown in our illustration. It will be seen that both pieces are made up of squares all of the same size—one 12x12 and the other 5x5. She proposes to join them together and make one square patchwork quilt, 13x13, but, of course, she will not cut any of the material—merely cut the stitches where necessary and join together again. What perplexes her is this. A friend assures her that there need be no more than four pieces in all to join up for the new quilt. Could you show her how this little needlework puzzle is to be solved in so few pieces?
-
Question 176 - LINOLEUM CUTTING
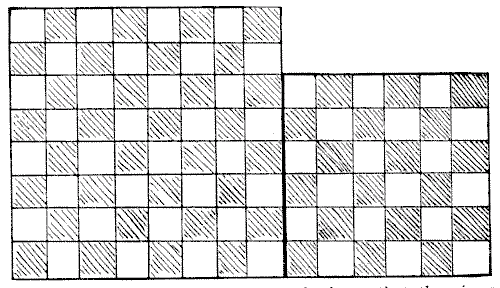 The diagram herewith represents two separate pieces of linoleum. The chequered pattern is not repeated at the back, so that the pieces cannot be turned over. The puzzle is to cut the two squares into four pieces so that they shall fit together and form one perfect square `10`×`10`, so that the pattern shall properly match, and so that the larger piece shall have as small a portion as possible cut from it.
The diagram herewith represents two separate pieces of linoleum. The chequered pattern is not repeated at the back, so that the pieces cannot be turned over. The puzzle is to cut the two squares into four pieces so that they shall fit together and form one perfect square `10`×`10`, so that the pattern shall properly match, and so that the larger piece shall have as small a portion as possible cut from it.
-
Question 177 - ANOTHER LINOLEUM PUZZLE
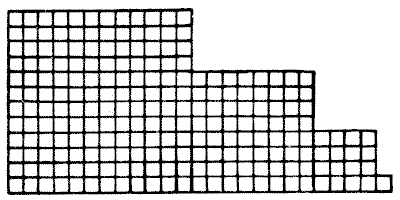
Can you cut this piece of linoleum into four pieces that will fit together and form a perfect square? Of course the cuts may only be made along the lines.
-
Question 178 - THE CARDBOARD BOX
This puzzle is not difficult, but it will be found entertaining to discover the simple rule for its solution. I have a rectangular cardboard box. The top has an area of `120` square inches, the side `96` square inches, and the end `80` square inches. What are the exact dimensions of the box?Topics:Geometry -> Solid Geometry / Geometry in Space Geometry -> Area Calculation Algebra -> Equations Algebra -> Word Problems -
Question 179 - STEALING THE BELL-ROPES
Two men broke into a church tower one night to steal the bell-ropes. The two ropes passed through holes in the wooden ceiling high above them, and they lost no time in climbing to the top. Then one man drew his knife and cut the rope above his head, in consequence of which he fell to the floor and was badly injured. His fellow-thief called out that it served him right for being such a fool. He said that he should have done as he was doing, upon which he cut the rope below the place at which he held on. Then, to his dismay, he found that he was in no better plight, for, after hanging on as long as his strength lasted, he was compelled to let go and fall beside his comrade. Here they were both found the next morning with their limbs broken. How far did they fall? One of the ropes when they found it was just touching the floor, and when you pulled the end to the wall, keeping the rope taut, it touched a point just three inches above the floor, and the wall was four feet from the rope when it hung at rest. How long was the rope from floor to ceiling? -
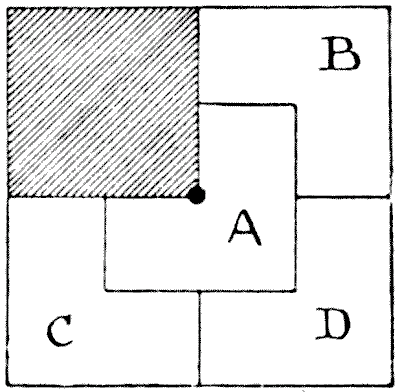
Question 180 - THE FOUR SONS
Readers will recognize the diagram as a familiar friend of their youth. A man possessed a square-shaped estate. He bequeathed to his widow the quarter of it that is shaded off. The remainder was to be divided equitably amongst his four sons, so that each should receive land of exactly the same area and exactly similar in shape. We are shown how this was done. But the remainder of the story is not so generally known. In the centre of the estate was a well, indicated by the dark spot, and Benjamin, Charles, and David complained that the division was not "equitable," since Alfred had access to this well, while they could not reach it without trespassing on somebody else's land. The puzzle is to show how the estate is to be apportioned so that each son shall have land of the same shape and area, and each have access to the well without going off his own land.