Geometry, Plane Geometry, Pythagorean Theorem
The Pythagorean Theorem is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right-angled triangle. It states that the square of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides (`a^2 + b^2 = c^2`). Questions involve applying this theorem to find side lengths.
-
Question
Given a cone (with an axis of symmetry in its center, perpendicular to its base) with a height of 6 and a base that is a circle with radius `sqrt2`. A cube is inscribed within the cone – it rests on the cone's base and all its upper vertices touch the cone. Find the side length of the cube. Justify your answer.
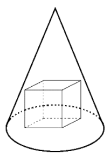 Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Solid Geometry / Geometry in Space Algebra -> Equations Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Pythagorean Theorem Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Triangles -> Triangle Similarity
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Solid Geometry / Geometry in Space Algebra -> Equations Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Pythagorean Theorem Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Triangles -> Triangle Similarity- Gillis Mathematical Olympiad, 2015-2016 Question 2
-
Question
Semicircles are constructed on the legs and hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle, as shown in the figure. Which area is larger—the hatched area or the shaded area?
 Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Triangles Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Circles Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Pythagorean Theorem
Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Triangles Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Circles Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Pythagorean Theorem -
Question
Shlomi has a flat box with a size of `5xx5` centimeters. Shlomi claims that any rectangle that can be stored in this box must have all its sides smaller than 5 centimeters. Is he right?
-
Right Triangles and a Square
Given a large number of congruent right triangles.
The side lengths of each triangle are 3, 4, and 5.
What is the maximum number of such triangles that can be placed inside a 20×20 square, such that they do not overlap?
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Triangles Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Pythagorean Theorem- Gillis Mathematical Olympiad, 2016-2017 Question 3
-
THE THREE VILLAGES
I set out the other day to ride in a motor-car from Acrefield to Butterford, but by mistake I took the road going via Cheesebury, which is nearer Acrefield than Butterford, and is twelve miles to the left of the direct road I should have travelled. After arriving at Butterford I found that I had gone thirty-five miles. What are the three distances between these villages, each being a whole number of miles? I may mention that the three roads are quite straight.Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Triangles Algebra -> Word Problems Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Pythagorean Theorem- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 69
-
THE SPOT ON THE TABLE
A boy, recently home from school, wished to give his father an exhibition of his precocity. He pushed a large circular table into the corner of the room, as shown in the illustration, so that it touched both walls, and he then pointed to a spot of ink on the extreme edge.
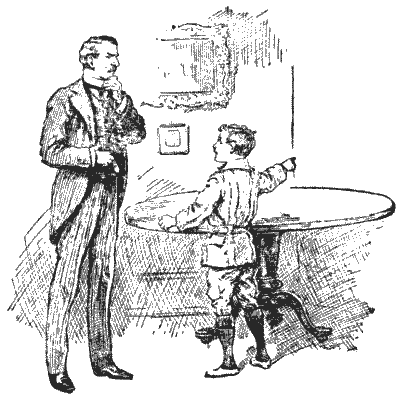
"Here is a little puzzle for you, pater," said the youth. "That spot is exactly eight inches from one wall and nine inches from the other. Can you tell me the diameter of the table without measuring it?"
The boy was overheard to tell a friend, "It fairly beat the guv'nor;" but his father is known to have remarked to a City acquaintance that he solved the thing in his head in a minute. I often wonder which spoke the truth.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Circles Algebra -> Equations Algebra -> Word Problems Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Pythagorean Theorem- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 97
-
THE BUN PUZZLE
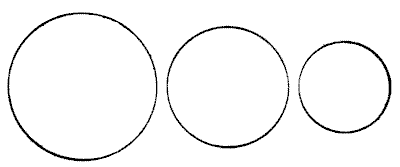 The three circles represent three buns, and it is simply required to show how these may be equally divided among four boys. The buns must be regarded as of equal thickness throughout and of equal thickness to each other. Of course, they must be cut into as few pieces as possible. To simplify it I will state the rather surprising fact that only five pieces are necessary, from which it will be seen that one boy gets his share in two pieces and the other three receive theirs in a single piece. I am aware that this statement "gives away" the puzzle, but it should not destroy its interest to those who like to discover the "reason why."
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Circles Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Pythagorean Theorem Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems
The three circles represent three buns, and it is simply required to show how these may be equally divided among four boys. The buns must be regarded as of equal thickness throughout and of equal thickness to each other. Of course, they must be cut into as few pieces as possible. To simplify it I will state the rather surprising fact that only five pieces are necessary, from which it will be seen that one boy gets his share in two pieces and the other three receive theirs in a single piece. I am aware that this statement "gives away" the puzzle, but it should not destroy its interest to those who like to discover the "reason why."
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Circles Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Pythagorean Theorem Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 148
-
ANOTHER JOINER'S PROBLEM
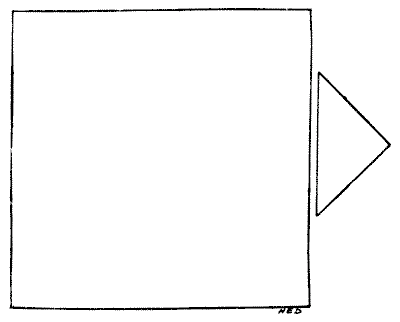 A joiner had two pieces of wood of the shapes and relative proportions shown in the diagram. He wished to cut them into as few pieces as possible so that they could be fitted together, without waste, to form a perfectly square table-top. How should he have done it? There is no necessity to give measurements, for if the smaller piece (which is half a square) be made a little too large or a little too small it will not affect the method of solution.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Pythagorean Theorem Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems
A joiner had two pieces of wood of the shapes and relative proportions shown in the diagram. He wished to cut them into as few pieces as possible so that they could be fitted together, without waste, to form a perfectly square table-top. How should he have done it? There is no necessity to give measurements, for if the smaller piece (which is half a square) be made a little too large or a little too small it will not affect the method of solution.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Pythagorean Theorem Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 152
-
THE SQUARE OF VENEER
The following represents a piece of wood in my possession, `5` in. square. By markings on the surface it is divided into twenty-five square inches. I want to discover a way of cutting this piece of wood into the fewest possible pieces that will fit together and form two perfect squares of different sizes and of known dimensions. But, unfortunately, at every one of the sixteen intersections of the cross lines a small nail has been driven in at some time or other, and my fret-saw will be injured if it comes in contact with any of these. I have therefore to find a method of doing the work that will not necessitate my cutting through any of those sixteen points. How is it to be done? Remember, the exact dimensions of the two squares must be given.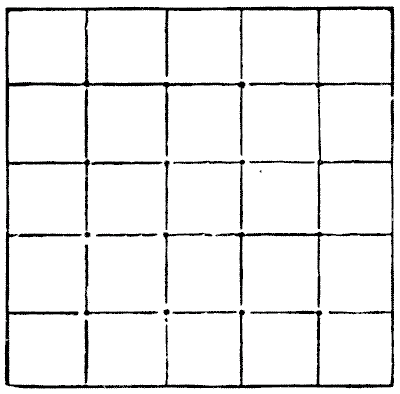 Sources:
Sources:
- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 159
-
LINOLEUM CUTTING
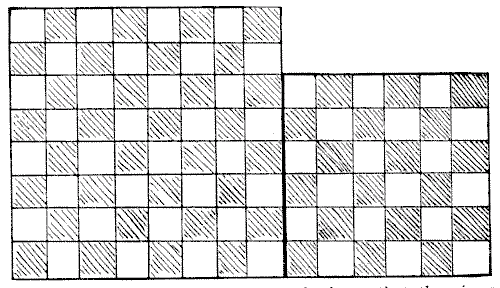 The diagram herewith represents two separate pieces of linoleum. The chequered pattern is not repeated at the back, so that the pieces cannot be turned over. The puzzle is to cut the two squares into four pieces so that they shall fit together and form one perfect square `10`×`10`, so that the pattern shall properly match, and so that the larger piece shall have as small a portion as possible cut from it.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Pythagorean Theorem Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems
The diagram herewith represents two separate pieces of linoleum. The chequered pattern is not repeated at the back, so that the pieces cannot be turned over. The puzzle is to cut the two squares into four pieces so that they shall fit together and form one perfect square `10`×`10`, so that the pattern shall properly match, and so that the larger piece shall have as small a portion as possible cut from it.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Pythagorean Theorem Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 176