Proof and Example
This category emphasizes the core mathematical activities of constructing rigorous arguments (proofs) to establish general truths, and using specific instances (examples) to illustrate concepts, test conjectures, or find counterexamples. Questions may ask for either or both.
Constructing an Example / Counterexample Proof by Contradiction-
Question
The game takes place on an infinite plane. One player moves the wolf, and another player moves K sheep. After the wolf's move, one of the sheep makes a move, then the wolf again, and so on. In one move, the wolf or a sheep cannot move more than one meter in any direction. Can the wolf always catch at least one sheep, regardless of the initial positions?
Sources: -
Question
A grasshopper can jump `80` centimeters forward or `50` centimeters backward. Can the grasshopper move away from its starting point in fewer than `7` jumps to a distance of exactly one meter and `70` cm?
-
Question
Is it possible to cut a triangle into four convex shapes: a triangle, a quadrilateral, a pentagon, and a hexagon?
-
Question
Given a sheet of paper of size `10×10` cm. Can you cut out a number of circles from this sheet such that the sum of their diameters is greater than `5` meters?
-
Question
A plane is colored with two colors (that is, every point on the plane is colored with one of these two colors). Prove that there exist two points on the plane at a distance of `1` such that they are both the same color.
-
Question
Is there a quadrilateral that can be cut into `6` parts by two straight cuts? Justify your answer or provide an example.
-
9 Kilograms of Rice
You have `9` kilograms of rice. How can you measure `2` kilograms of rice using three weighings on a balance scale and using two weights: one of `200` grams and one of `50` grams?
-
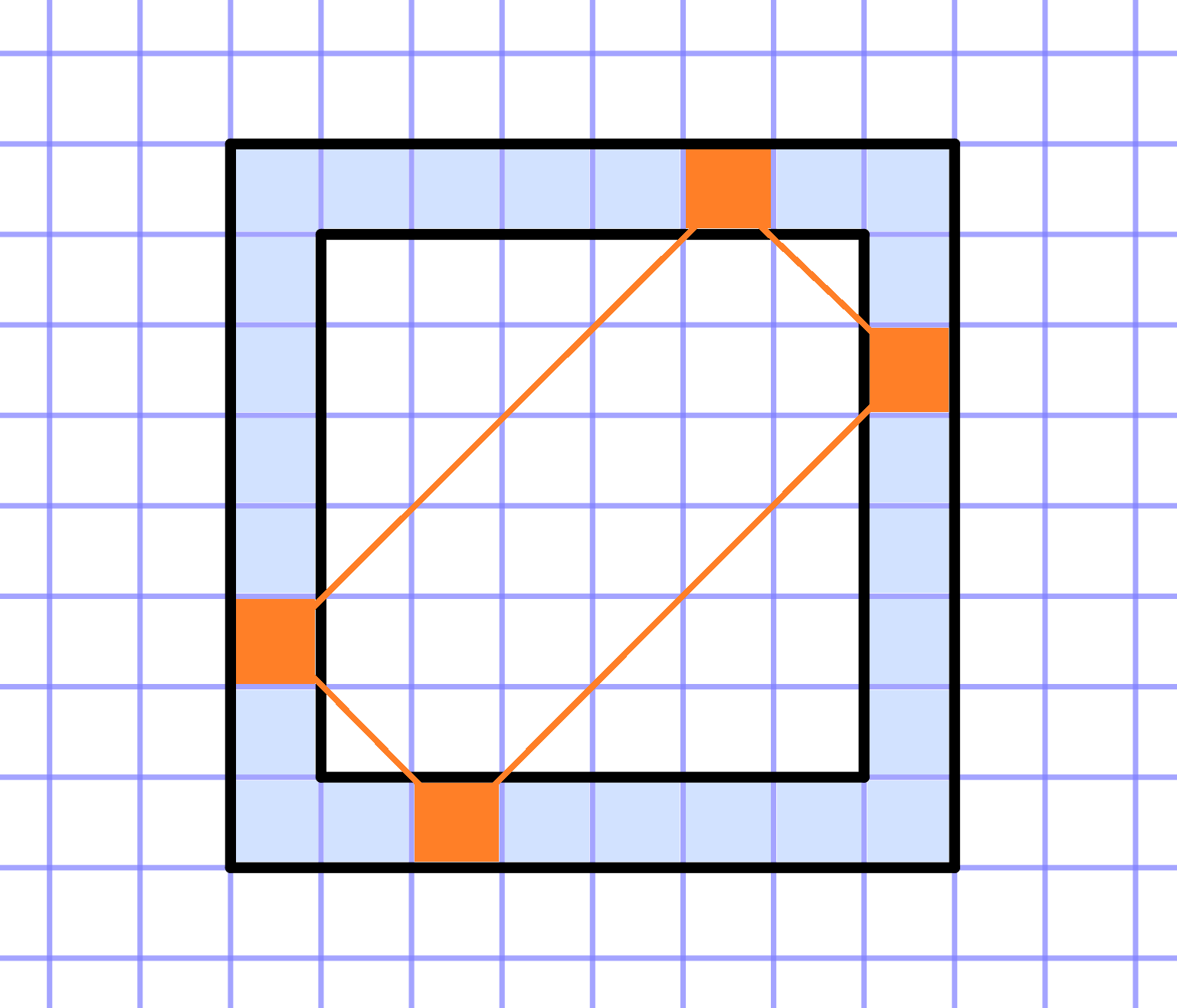
Frame
On a grid paper, a square of size `NxxN` is given. Consider its frame with a width of one square. It consists of `4*(N-1)` squares.
Can you write `4*(N-1)` consecutive integers (not necessarily positive) in the squares of the frame, such that the following condition holds:
For every rectangle whose vertices are on the frame and whose sides are parallel to the diagonals of the original square, the sum of the numbers at the vertices is equal to a constant value. This also includes the "degenerate" rectangles of zero width that coincide with the diagonals of the square - in this case, simply sum the two numbers at the opposite vertices of the square.
For:
a. `N=3`
b. `N=4`
c. `N=5`
 Sources:Topics:Arithmetic Number Theory -> Division -> Parity (Even/Odd) Proof and Example -> Constructing an Example / Counterexample Algebra -> Sequences -> Arithmetic Progression / Arithmetic Sequence Combinatorics -> Case Analysis / Checking Cases -> Processes / Procedures
Sources:Topics:Arithmetic Number Theory -> Division -> Parity (Even/Odd) Proof and Example -> Constructing an Example / Counterexample Algebra -> Sequences -> Arithmetic Progression / Arithmetic Sequence Combinatorics -> Case Analysis / Checking Cases -> Processes / Procedures- Tournament of Towns, 1983-1984, Fall, Practice Version, Grades 9-10 Question 3 Points 2+3+4
-
Question
A. You have a large jug of 12 liters of olive oil and two empty smaller vessels, one of 5 liters and one of 8 liters. Can you divide the oil you have into two equal parts, if you only have these vessels and no additional measuring tools?
B. The same question, but instead of the 5-liter vessel, you have a 4-liter vessel.
Topics:Number Theory -> Modular Arithmetic / Remainder Arithmetic -> Divisibility Rules Combinatorics -> Invariants Logic -> Reasoning / Logic Number Theory -> Division -> Parity (Even/Odd) Proof and Example -> Constructing an Example / Counterexample Number Theory -> Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and Least Common Multiple (LCM) -> Euclidean Algorithm Combinatorics -> Case Analysis / Checking Cases -> Processes / Procedures Proof and Example -> Proof by Contradiction -
Question
`120` identical spheres are arranged in the shape of a triangular pyramid. How many layers are there in the pyramid?
Note: This is a pyramid, which is a three-dimensional shape, and not a triangle in a plane.
Topics:Geometry -> Solid Geometry / Geometry in Space Arithmetic Logic -> Reasoning / Logic Proof and Example -> Constructing an Example / Counterexample Algebra -> Sequences -> Arithmetic Progression / Arithmetic Sequence Algebra -> Sequences -> Complete/Continue the Sequence Number Theory -> Triangular Numbers