Algebra, Equations
An equation is a statement that two mathematical expressions are equal. Solving an equation involves finding the values of variables that make the statement true. Questions cover various types: linear, quadratic, polynomial, rational, radical, and systems of equations.
Diophantine Equations-
REAPING THE CORN
A farmer had a square cornfield. The corn was all ripe for reaping, and, as he was short of men, it was arranged that he and his son should share the work between them. The farmer first cut one rod wide all round the square, thus leaving a smaller square of standing corn in the middle of the field. "Now," he said to his son, "I have cut my half of the field, and you can do your share." The son was not quite satisfied as to the proposed division of labour, and as the village schoolmaster happened to be passing, he appealed to that person to decide the matter. He found the farmer was quite correct, provided there was no dispute as to the size of the field, and on this point they were agreed. Can you tell the area of the field, as that ingenious schoolmaster succeeded in doing? Sources:- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 111
-
CURIOUS NUMBERS
The number `48` has this peculiarity, that if you add `1` to it the result is a square number (`49`, the square of `7`), and if you add `1` to its half, you also get a square number (`25`, the square of `5`). Now, there is no limit to the numbers that have this peculiarity, and it is an interesting puzzle to find three more of them—the smallest possible numbers. What are they? Sources:- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 114
-
A PRINTER'S ERROR
In a certain article a printer had to set up the figures `5^4xx2^3`, which, of course, means that the fourth power of `5` (`625`) is to be multiplied by the cube of `2` (`8`), the product of which is `5,000`. But he printed `5^4xx2^3` as `5\ 4\ 2\ 3`, which is not correct. Can you place four digits in the manner shown, so that it will be equally correct if the printer sets it up aright or makes the same blunder?
Sources:- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 115
-
RACKBRANE'S LITTLE LOSS
Professor Rackbrane was spending an evening with his old friends, Mr. and Mrs. Potts, and they engaged in some game (he does not say what game) of cards. The professor lost the first game, which resulted in doubling the money that both Mr. and Mrs. Potts had laid on the table. The second game was lost by Mrs. Potts, which doubled the money then held by her husband and the professor. Curiously enough, the third game was lost by Mr. Potts, and had the effect of doubling the money then held by his wife and the professor. It was then found that each person had exactly the same money, but the professor had lost five shillings in the course of play. Now, the professor asks, what was the sum of money with which he sat down at the table? Can you tell him? Sources:- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 119
-
THE FARMER AND HIS SHEEP
Farmer Longmore had a curious aptitude for arithmetic, and was known in his district as the "mathematical farmer." The new vicar was not aware of this fact when, meeting his worthy parishioner one day in the lane, he asked him in the course of a short conversation, "Now, how many sheep have you altogether?" He was therefore rather surprised at Longmore's answer, which was as follows: "You can divide my sheep into two different parts, so that the difference between the two numbers is the same as the difference between their squares. Maybe, Mr. Parson, you will like to work out the little sum for yourself."
Can the reader say just how many sheep the farmer had? Supposing he had possessed only twenty sheep, and he divided them into the two parts `12` and `8`. Now, the difference between their squares, `144` and `64`, is `80`. So that will not do, for `4` and `80` are certainly not the same. If you can find numbers that work out correctly, you will know exactly how many sheep Farmer Longmore owned.
Sources:- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 120
-
THE SEE-SAW PUZZLE
Necessity is, indeed, the mother of invention. I was amused the other day in watching a boy who wanted to play see-saw and, in his failure to find another child to share the sport with him, had been driven back upon the ingenious resort of tying a number of bricks to one end of the plank to balance his weight at the other.
As a matter of fact, he just balanced against sixteen bricks, when these were fixed to the short end of plank, but if he fixed them to the long end of plank he only needed eleven as balance.
Now, what was that boy's weight, if a brick weighs equal to a three-quarter brick and three-quarters of a pound?
Sources:- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 122
-
THE ARTILLERYMEN'S DILEMMA
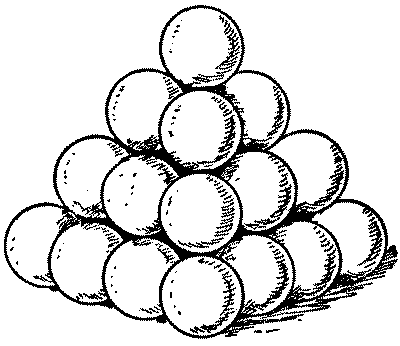 "All cannon-balls are to be piled in square pyramids," was the order issued to the regiment. This was done. Then came the further order, "All pyramids are to contain a square number of balls." Whereupon the trouble arose. "It can't be done," said the major. "Look at this pyramid, for example; there are sixteen balls at the base, then nine, then four, then one at the top, making thirty balls in all. But there must be six more balls, or five fewer, to make a square number." "It must be done," insisted the general. "All you have to do is to put the right number of balls in your pyramids." "I've got it!" said a lieutenant, the mathematical genius of the regiment. "Lay the balls out singly." "Bosh!" exclaimed the general. "You can't pile one ball into a pyramid!" Is it really possible to obey both orders?
Sources:
"All cannon-balls are to be piled in square pyramids," was the order issued to the regiment. This was done. Then came the further order, "All pyramids are to contain a square number of balls." Whereupon the trouble arose. "It can't be done," said the major. "Look at this pyramid, for example; there are sixteen balls at the base, then nine, then four, then one at the top, making thirty balls in all. But there must be six more balls, or five fewer, to make a square number." "It must be done," insisted the general. "All you have to do is to put the right number of balls in your pyramids." "I've got it!" said a lieutenant, the mathematical genius of the regiment. "Lay the balls out singly." "Bosh!" exclaimed the general. "You can't pile one ball into a pyramid!" Is it really possible to obey both orders?
Sources:
- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 138
-
THE CARDBOARD BOX
This puzzle is not difficult, but it will be found entertaining to discover the simple rule for its solution. I have a rectangular cardboard box. The top has an area of `120` square inches, the side `96` square inches, and the end `80` square inches. What are the exact dimensions of the box?Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Solid Geometry / Geometry in Space Geometry -> Area Calculation Algebra -> Equations Algebra -> Word Problems- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 178
-
THE GARDEN PUZZLE
Professor Rackbrain tells me that he was recently smoking a friendly pipe under a tree in the garden of a country acquaintance. The garden was enclosed by four straight walls, and his friend informed him that he had measured these and found the lengths to be `80, 45, 100`, and `63` yards respectively. "Then," said the professor, "we can calculate the exact area of the garden." "Impossible," his host replied, "because you can get an infinite number of different shapes with those four sides." "But you forget," Rackbrane said, with a twinkle in his eye, "that you told me once you had planted this tree equidistant from all the four corners of the garden." Can you work out the garden's area?Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Circles Algebra -> Equations Algebra -> Word Problems- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 182
-
THE CLOTHES LINE PUZZLE
A boy tied a clothes line from the top of each of two poles to the base of the other. He then proposed to his father the following question. As one pole was exactly seven feet above the ground and the other exactly five feet, what was the height from the ground where the two cords crossed one another? Sources:- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 186