Geometry, Area Calculation
This topic focuses on methods for determining the size of a two-dimensional surface or region. Questions involve calculating the areas of various geometric shapes like triangles, quadrilaterals, circles, and more complex composite figures, often requiring application of specific formulas.
-
Question
In the figure, a semicircle is shown with three circles inscribed within it: the large circle, tangent to the diameter of the semicircle at its center, and two smaller circles on the sides, symmetrically arranged. Which area is larger: the shaded area or the unshaded area?
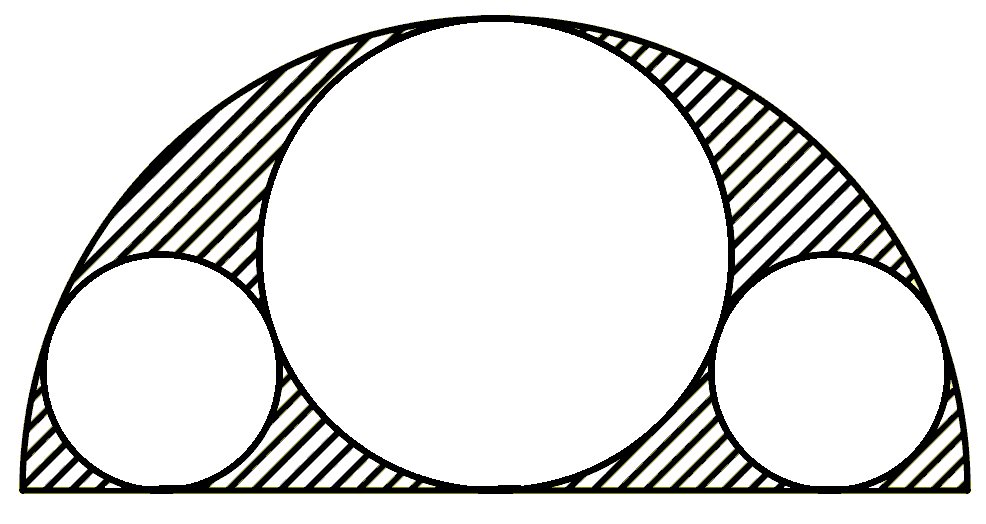 Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Circles Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry
Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Circles Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry -
Quarter Yin-Yang
The shape in the drawing is constructed as follows: Divide the diameter of a semicircle into two equal parts, and construct two additional semicircles on them as diameters: one inwards, and one outwards.
Divide the shape into two congruent parts.
Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Circles Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems -
Question
Given a sheet of paper of size `10×10` cm. Can you cut out a number of circles from this sheet such that the sum of their diameters is greater than `5` meters?
-
Question
It is known that all the angles of the given shape are right angles. Cut the shape into two polygons of equal area. You are only allowed to use an unmarked ruler.
-
Question
Two congruent triangles form a Star of David as depicted in the drawing. Prove that the shaded area is equal to the hatched area.
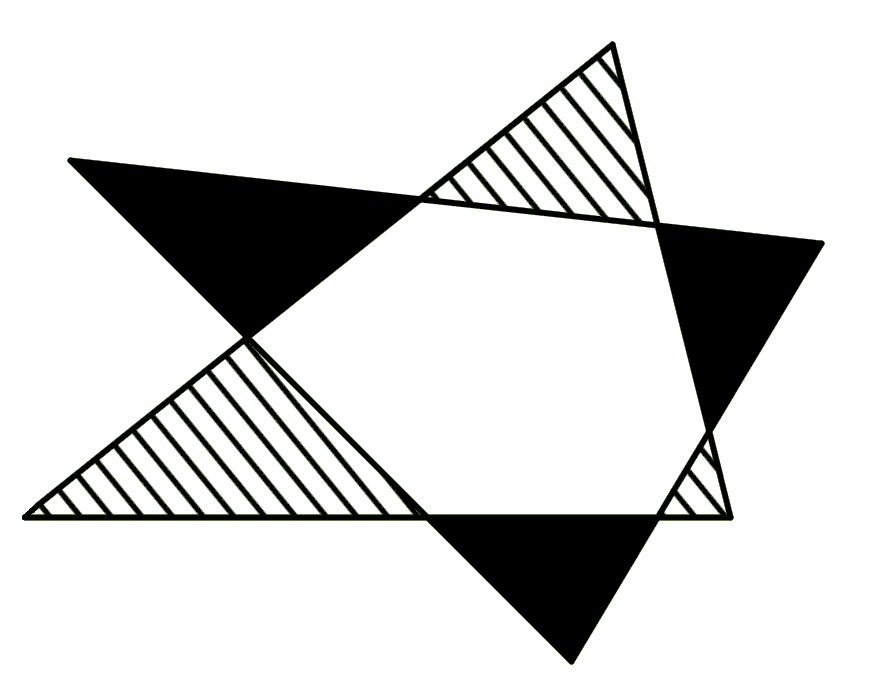 Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Proof and Example Set Theory Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Triangles -> Triangle Congruence
Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Proof and Example Set Theory Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Triangles -> Triangle Congruence -
Question
Can you fit a rectangle of size `5xx5` into a rectangle of size `4xx6`?
Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation -
Area of the Shape
Given a grid paper where the area of each square is one unit area. Find the area of the shape (in unit areas)
Sources: -
Question
Inside a square with side length 1, `n>=101` points are marked, such that no three are collinear. A triangle is called marked if its vertices are marked points. Prove that the area of one of the marked triangles is less than `1/100`
Sources: -
Hexagon
In the diagram, there is a regular hexagon. By what factor is the area of the white region larger than the area of the shaded region?
(A regular hexagon is a hexagon where all sides are equal and all angles are equal.)
Sources: -
Products of Areas
In the figure, there is a rectangle and a point inside it. Two segments are drawn through the point, parallel to the sides of the rectangle, dividing the rectangle into 4 smaller rectangles.
Prove that the product of the areas of the shaded rectangles inside the rectangle is equal to the product of the areas of the unshaded rectangles inside the rectangle.Sources:




