Algebra
Algebra is a broad branch of mathematics that uses symbols (usually letters) to represent numbers and to state rules and relationships. It involves manipulating expressions, solving equations and inequalities, and studying functions and structures. Questions cover a wide range of these topics.
Algebraic Techniques Equations Inequalities Word Problems Sequences-
THE FIVE BRIGANDS
The five Spanish brigands, Alfonso, Benito, Carlos, Diego, and Esteban, were counting their spoils after a raid, when it was found that they had captured altogether exactly `200` doubloons. One of the band pointed out that if Alfonso had twelve times as much, Benito three times as much, Carlos the same amount, Diego half as much, and Esteban one-third as much, they would still have altogether just `200` doubloons. How many doubloons had each?
There are a good many equally correct answers to this question. Here is one of them:
A 6 × 12 = 72 B 12 × 3 = 36 C 17 × 1 = 17 D 120 × ½ = 60 E 45 × 1/3 = 15 200 200 The puzzle is to discover exactly how many different answers there are, it being understood that every man had something and that there is to be no fractional money—only doubloons in every case.
This problem, worded somewhat differently, was propounded by Tartaglia (died `1559`), and he flattered himself that he had found one solution; but a French mathematician of note (M.A. Labosne), in a recent work, says that his readers will be astonished when he assures them that there are `6,639` different correct answers to the question. Is this so? How many answers are there?
Sources:Topics:Number Theory Arithmetic Algebra -> Word Problems Algebra -> Sequences -> Arithmetic Progression / Arithmetic Sequence Combinatorics -> Case Analysis / Checking Cases -> Processes / Procedures Algebra -> Equations -> Diophantine Equations- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 133
-
THE STONEMASON'S PROBLEM
A stonemason once had a large number of cubic blocks of stone in his yard, all of exactly the same size. He had some very fanciful little ways, and one of his queer notions was to keep these blocks piled in cubical heaps, no two heaps containing the same number of blocks. He had discovered for himself (a fact that is well known to mathematicians) that if he took all the blocks contained in any number of heaps in regular order, beginning with the single cube, he could always arrange those on the ground so as to form a perfect square. This will be clear to the reader, because one block is a square, `1+8 = 9` is a square, `1+8+27=36` is a square, `1+8+27+64=100` is a square, and so on. In fact, the sum of any number of consecutive cubes, beginning always with `1`, is in every case a square number.
One day a gentleman entered the mason's yard and offered him a certain price if he would supply him with a consecutive number of these cubical heaps which should contain altogether a number of blocks that could be laid out to form a square, but the buyer insisted on more than three heaps and declined to take the single block because it contained a flaw. What was the smallest possible number of blocks of stone that the mason had to supply?
Sources:- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 135
-
THE ARTILLERYMEN'S DILEMMA
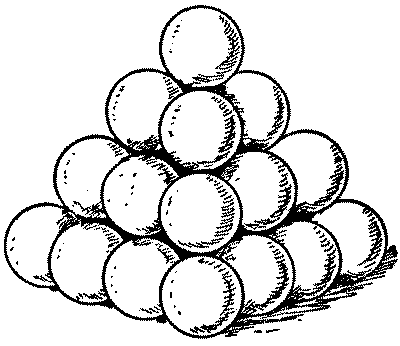 "All cannon-balls are to be piled in square pyramids," was the order issued to the regiment. This was done. Then came the further order, "All pyramids are to contain a square number of balls." Whereupon the trouble arose. "It can't be done," said the major. "Look at this pyramid, for example; there are sixteen balls at the base, then nine, then four, then one at the top, making thirty balls in all. But there must be six more balls, or five fewer, to make a square number." "It must be done," insisted the general. "All you have to do is to put the right number of balls in your pyramids." "I've got it!" said a lieutenant, the mathematical genius of the regiment. "Lay the balls out singly." "Bosh!" exclaimed the general. "You can't pile one ball into a pyramid!" Is it really possible to obey both orders?
Sources:
"All cannon-balls are to be piled in square pyramids," was the order issued to the regiment. This was done. Then came the further order, "All pyramids are to contain a square number of balls." Whereupon the trouble arose. "It can't be done," said the major. "Look at this pyramid, for example; there are sixteen balls at the base, then nine, then four, then one at the top, making thirty balls in all. But there must be six more balls, or five fewer, to make a square number." "It must be done," insisted the general. "All you have to do is to put the right number of balls in your pyramids." "I've got it!" said a lieutenant, the mathematical genius of the regiment. "Lay the balls out singly." "Bosh!" exclaimed the general. "You can't pile one ball into a pyramid!" Is it really possible to obey both orders?
Sources:
- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 138
-
THE DUTCHMEN'S WIVES
I wonder how many of my readers are acquainted with the puzzle of the "Dutchmen's Wives"—in which you have to determine the names of three men's wives, or, rather, which wife belongs to each husband. Some thirty years ago it was "going the rounds," as something quite new, but I recently discovered it in the Ladies' Diary for `1739-40`, so it was clearly familiar to the fair sex over one hundred and seventy years ago. How many of our mothers, wives, sisters, daughters, and aunts could solve the puzzle to-day? A far greater proportion than then, let us hope.
Three Dutchmen, named Hendrick, Elas, and Cornelius, and their wives, Gurtrün, Katrün, and Anna, purchase hogs. Each buys as many as he (or she) gives shillings for one. Each husband pays altogether three guineas more than his wife. Hendrick buys twenty-three more hogs than Katrün, and Elas eleven more than Gurtrün. Now, what was the name of each man's wife?
 Sources:Topics:Number Theory -> Prime Numbers Arithmetic Algebra -> Word Problems Algebra -> Equations -> Diophantine Equations
Sources:Topics:Number Theory -> Prime Numbers Arithmetic Algebra -> Word Problems Algebra -> Equations -> Diophantine Equations- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 139
-
FIND ADA'S SURNAME
This puzzle closely resembles the last one, my remarks on the solution of which the reader may like to apply in another case. It was recently submitted to a Sydney evening newspaper that indulges in "intellect sharpeners," but was rejected with the remark that it is childish and that they only published problems capable of solution! Five ladies, accompanied by their daughters, bought cloth at the same shop. Each of the ten paid as many farthings per foot as she bought feet, and each mother spent `8`s. `5`¼d. more than her daughter. Mrs. Robinson spent `6`s. more than Mrs. Evans, who spent about a quarter as much as Mrs. Jones. Mrs. Smith spent most of all. Mrs. Brown bought `21` yards more than Bessie—one of the girls. Annie bought `16` yards more than Mary and spent £`3, 0`s. `8`d. more than Emily. The Christian name of the other girl was Ada. Now, what was her surname? Sources:- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 140
-
SATURDAY MARKETING
Here is an amusing little case of marketing which, although it deals with a good many items of money, leads up to a question of a totally different character. Four married couples went into their village on a recent Saturday night to do a little marketing. They had to be very economical, for among them they only possessed forty shilling coins. The fact is, Ann spent `1`s., Mary spent `2`s., Jane spent `3`s., and Kate spent `4`s. The men were rather more extravagant than their wives, for Ned Smith spent as much as his wife, Tom Brown twice as much as his wife, Bill Jones three times as much as his wife, and Jack Robinson four times as much as his wife. On the way home somebody suggested that they should divide what coin they had left equally among them. This was done, and the puzzling question is simply this: What was the surname of each woman? Can you pair off the four couples?
Sources:- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 141
-
THE SQUARE OF VENEER
The following represents a piece of wood in my possession, `5` in. square. By markings on the surface it is divided into twenty-five square inches. I want to discover a way of cutting this piece of wood into the fewest possible pieces that will fit together and form two perfect squares of different sizes and of known dimensions. But, unfortunately, at every one of the sixteen intersections of the cross lines a small nail has been driven in at some time or other, and my fret-saw will be injured if it comes in contact with any of these. I have therefore to find a method of doing the work that will not necessitate my cutting through any of those sixteen points. How is it to be done? Remember, the exact dimensions of the two squares must be given.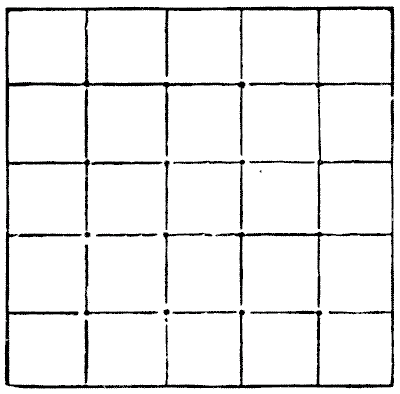 Sources:
Sources:
- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 159
-
THE POTATO PUZZLE
Take a circular slice of potato, place it on the table, and see into how large a number of pieces you can divide it with six cuts of a knife. Of course you must not readjust the pieces or pile them after a cut. What is the greatest number of pieces you can make?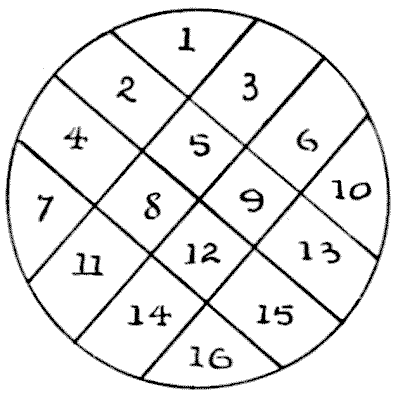 The illustration shows how to make sixteen pieces. This can, of course, be easily beaten.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry Algebra -> Sequences Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems
The illustration shows how to make sixteen pieces. This can, of course, be easily beaten.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry Algebra -> Sequences Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 164
-
THE CARDBOARD BOX
This puzzle is not difficult, but it will be found entertaining to discover the simple rule for its solution. I have a rectangular cardboard box. The top has an area of `120` square inches, the side `96` square inches, and the end `80` square inches. What are the exact dimensions of the box?Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Solid Geometry / Geometry in Space Geometry -> Area Calculation Algebra -> Equations Algebra -> Word Problems- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 178
-
STEALING THE BELL-ROPES
Two men broke into a church tower one night to steal the bell-ropes. The two ropes passed through holes in the wooden ceiling high above them, and they lost no time in climbing to the top. Then one man drew his knife and cut the rope above his head, in consequence of which he fell to the floor and was badly injured. His fellow-thief called out that it served him right for being such a fool. He said that he should have done as he was doing, upon which he cut the rope below the place at which he held on. Then, to his dismay, he found that he was in no better plight, for, after hanging on as long as his strength lasted, he was compelled to let go and fall beside his comrade. Here they were both found the next morning with their limbs broken. How far did they fall? One of the ropes when they found it was just touching the floor, and when you pulled the end to the wall, keeping the rope taut, it touched a point just three inches above the floor, and the wall was four feet from the rope when it hung at rest. How long was the rope from floor to ceiling? Sources:- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 179