Algebra
Algebra is a broad branch of mathematics that uses symbols (usually letters) to represent numbers and to state rules and relationships. It involves manipulating expressions, solving equations and inequalities, and studying functions and structures. Questions cover a wide range of these topics.
Algebraic Techniques Equations Inequalities Word Problems Sequences-
Question
Is the following number prime?
`4^9 + 6^10 + 3^20`
-
Question
The distinct real numbers `x` and `y` satisfy the equation:
`x^2 – 2000x = y^2 – 2000y`
Find the sum of `x` and `y`.
-
Question
Solve the equation:
`(x + 2010)(x + 2011)(x + 2012) = (x + 2011)(x + 2012)(x + 2013) `
Sources: -
Question
Given a cone (with an axis of symmetry in its center, perpendicular to its base) with a height of 6 and a base that is a circle with radius `sqrt2`. A cube is inscribed within the cone – it rests on the cone's base and all its upper vertices touch the cone. Find the side length of the cube. Justify your answer.
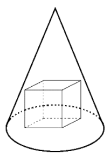 Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Solid Geometry / Geometry in Space Algebra -> Equations Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Pythagorean Theorem Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Triangles -> Triangle Similarity
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Solid Geometry / Geometry in Space Algebra -> Equations Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Pythagorean Theorem Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Triangles -> Triangle Similarity- Gillis Mathematical Olympiad, 2015-2016 Question 2
-
Question
Given an `M times N` matrix, where each cell contains a real number. It is known that the sum of the numbers in each row and each column is equal to `1`.
Prove that `M = N`.
Topics:Combinatorics -> Double Counting Logic -> Reasoning / Logic Algebra -> Inequalities -> Averages / Means -
Question
Given a positive integer N, consider the following process: Let `S(N)` denote the sum of the digits of N. Take the sum of the digits of `S(N)`. Repeat this operation until a single-digit number is obtained. We call the number of times we performed the above process until we obtained a single-digit number the "depth" of N. For example, the depth of 49 is `S(49)=13 -> S(13)=4`, the operation was performed twice (and the depth of 45 is 1).
a) Prove that for every number N there is indeed a finite depth, that is, a single-digit number is always obtained at some stage of the process.
b) Let `x(n)` denote the minimum number (with the smallest value) with depth N. Find the remainder of `x(5776)` when divided by 6. Justify your answer!
c) Find the remainder of the number `x(5776) - x(5708)` when divided by 2016. Justify your answer!
Sources:Topics:Number Theory -> Modular Arithmetic / Remainder Arithmetic Combinatorics -> Induction (Mathematical Induction) Algebra -> Sequences -> Arithmetic Progression / Arithmetic Sequence- Gillis Mathematical Olympiad, 2015-2016 Question 3
-
Question
Prove that any real number can be written as the sum of 9 numbers, each of which is composed only of the digits 0 and 7.
Sources: -
Coins and Cakes
Miriam has coins of two shekels and of five shekels.
If she pays only with two-shekel coins, she will be 60 shekels short of buying 4 cakes.
If she pays only with five-shekel coins, she will be 60 shekels short of buying 5 cakes.
In total, she is 60 shekels short of buying 6 cakes. How much does a cake cost?
Sources:- Beno Arbel Olympiad, 2013, Grade 7 Question 2
-
Question
How many solutions in natural numbers are there to the equation `(2013 - x)(2013-y)=2013^2`?
Sources:Topics:Number Theory -> Prime Numbers -> Prime Factorization Algebra -> Equations -> Diophantine Equations- Beno Arbel Olympiad, 2013, Grade 7 Question 6
-
Question
A box contains pencils in three colors: red, green, and blue, totaling `20` pencils. There are `6` times more blue pencils than green pencils. There are fewer red pencils than green pencils. How many red pencils are in the box?