Combinatorics, Combinatorial Geometry
Combinatorial Geometry explores the connections between combinatorics and geometry. It deals with problems about arrangements, configurations, and properties of discrete geometric objects (points, lines, polygons). Questions often involve counting, existence proofs, and geometric inequalities.
Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry-
THE QUEEN'S JOURNEY
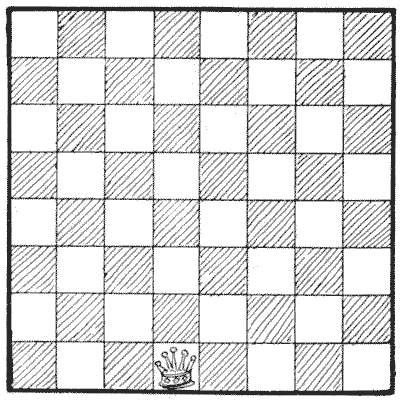 Place the queen on her own square, as shown in the illustration, and then try to discover the greatest distance that she can travel over the board in five queen's moves without passing over any square a second time. Mark the queen's path on the board, and note carefully also that she must never cross her own track. It seems simple enough, but the reader may find that he has tripped.
Sources:
Place the queen on her own square, as shown in the illustration, and then try to discover the greatest distance that she can travel over the board in five queen's moves without passing over any square a second time. Mark the queen's path on the board, and note carefully also that she must never cross her own track. It seems simple enough, but the reader may find that he has tripped.
Sources:
- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 333
-
THE FOUR KNIGHTS' TOURS
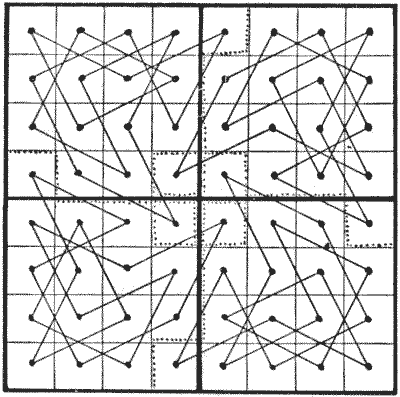 I will repeat that if a chessboard be cut into four equal parts, as indicated by the dark lines in the illustration, it is not possible to perform a knight's tour, either re-entrant or not, on one of the parts. The best re-entrant attempt is shown, in which each knight has to trespass twice on other parts. The puzzle is to cut the board differently into four parts, each of the same size and shape, so that a re-entrant knight's tour may be made on each part. Cuts along the dotted lines will not do, as the four central squares of the board would be either detached or hanging on by a mere thread.
Sources:
I will repeat that if a chessboard be cut into four equal parts, as indicated by the dark lines in the illustration, it is not possible to perform a knight's tour, either re-entrant or not, on one of the parts. The best re-entrant attempt is shown, in which each knight has to trespass twice on other parts. The puzzle is to cut the board differently into four parts, each of the same size and shape, so that a re-entrant knight's tour may be made on each part. Cuts along the dotted lines will not do, as the four central squares of the board would be either detached or hanging on by a mere thread.
Sources:
- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 339
-
THE TWO ROOKS
This is a puzzle game for two players. Each player has a single rook. The first player places his rook on any square of the board that he may choose to select, and then the second player does the same. They now play in turn, the point of each play being to capture the opponent's rook. But in this game you cannot play through a line of attack without being captured. That is to say, if in the diagram it is Black's turn to play, he cannot move his rook to his king's knight's square, or to his king's rook's square, because he would enter the "line of fire" when passing his king's bishop's square. For the same reason he cannot move to his queen's rook's seventh or eighth squares. Now, the game can never end in a draw. Sooner or later one of the rooks must fall, unless, of course, both players commit the absurdity of not trying to win. The trick of winning is ridiculously simple when you know it. Can you solve the puzzle?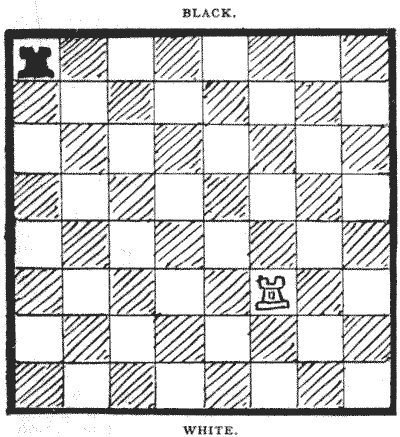 Sources:Topics:Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry Combinatorics -> Invariants Combinatorics -> Game Theory Logic -> Reasoning / Logic Combinatorics -> Colorings -> Chessboard Coloring
Sources:Topics:Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry Combinatorics -> Invariants Combinatorics -> Game Theory Logic -> Reasoning / Logic Combinatorics -> Colorings -> Chessboard Coloring- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 393
-
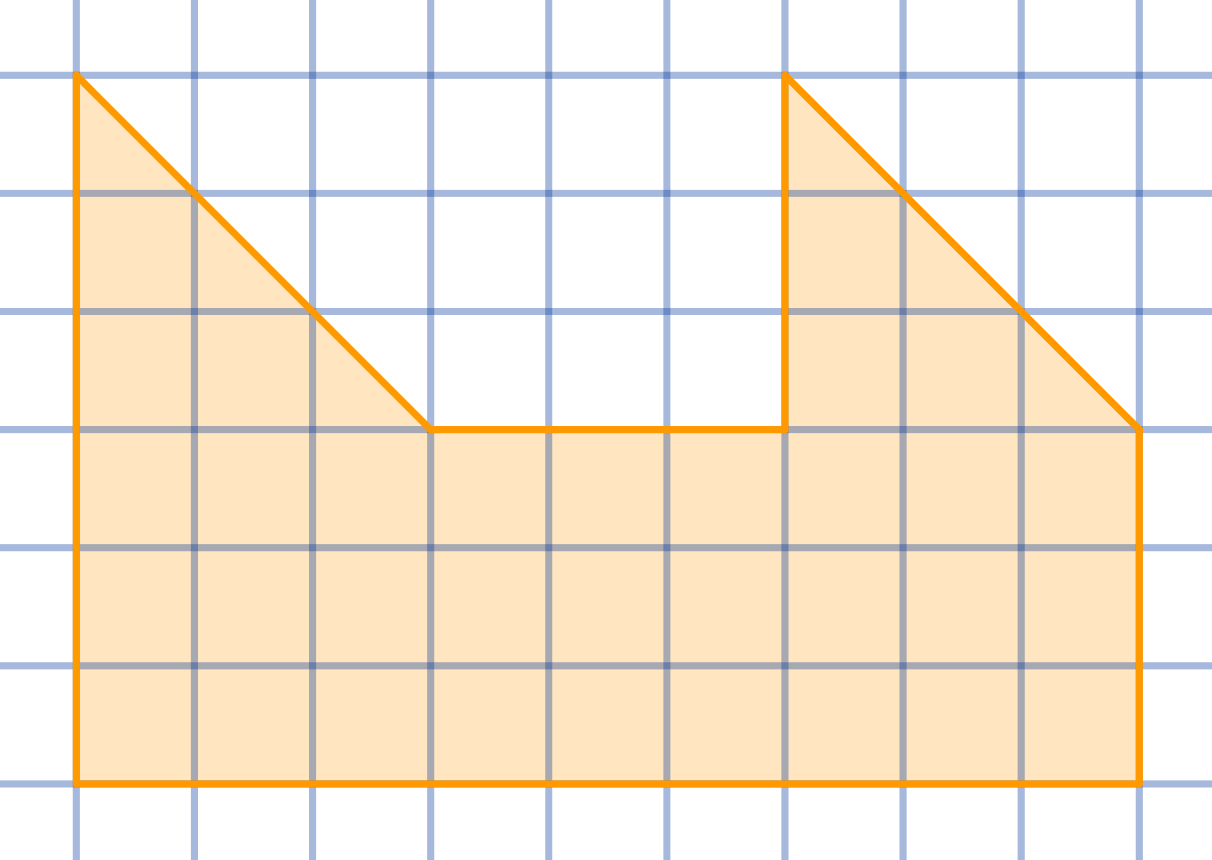
Question
Cut the given shape into two congruent parts:
 Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries)
Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries) -
Question
Cut the given shape into two congruent parts:
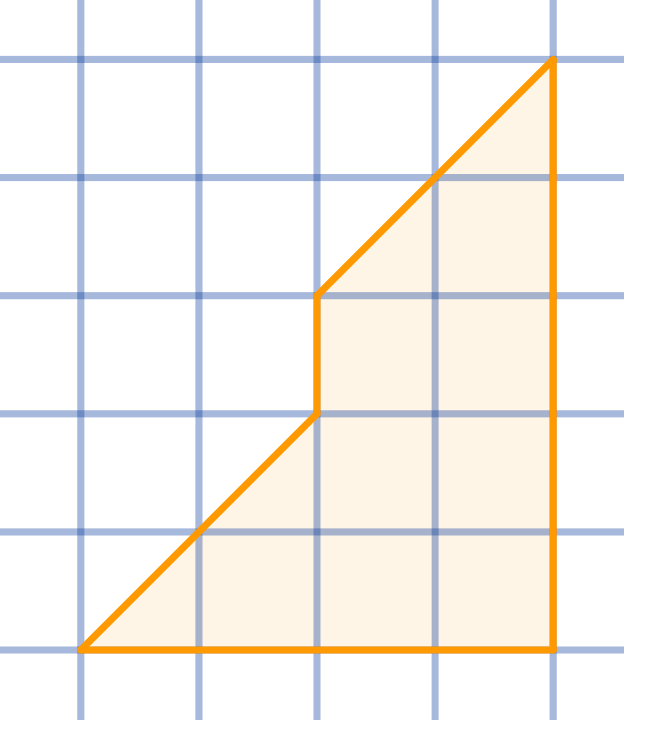 Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries)
Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries) -
Question
Cut the given shape into three congruent parts:
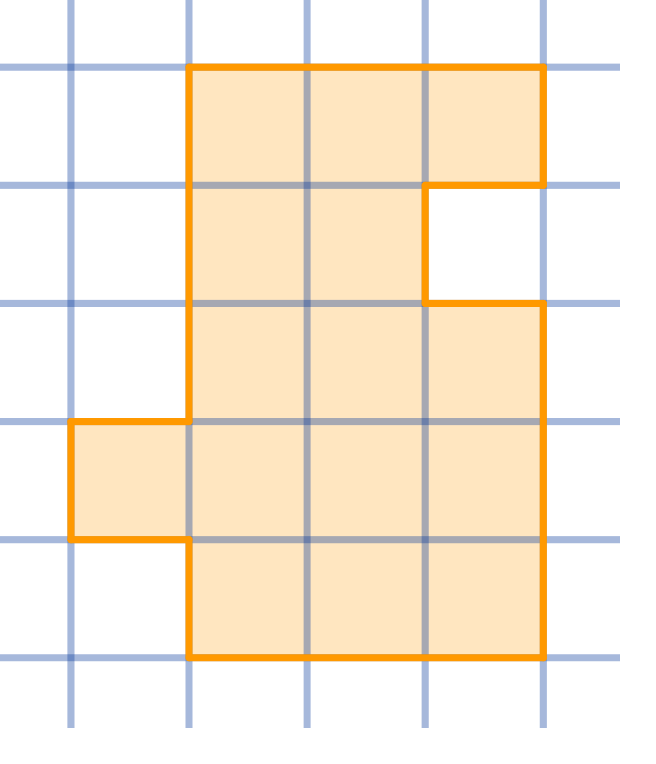 Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries)
Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries) -
Question
Cut the given shape into three congruent parts:
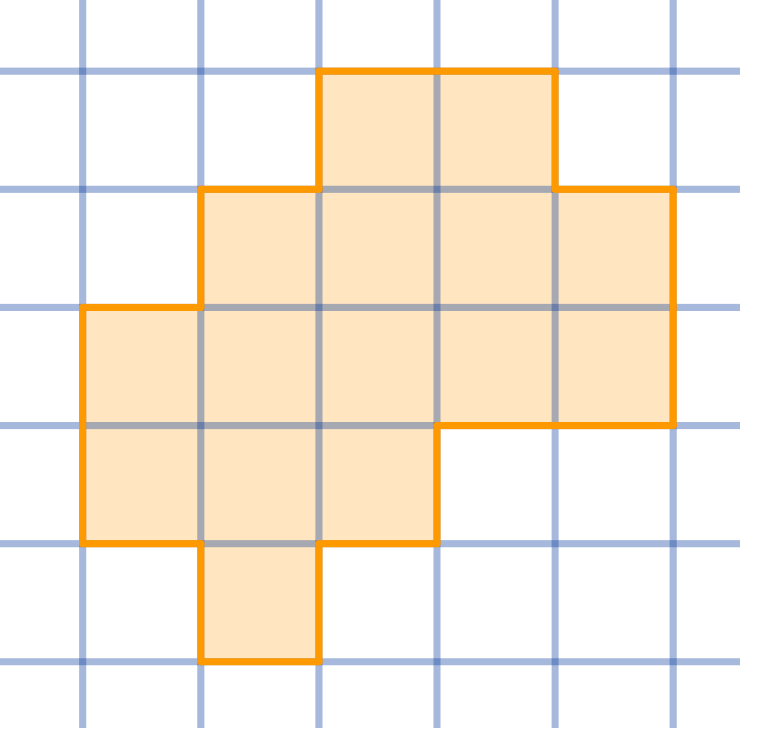 Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries)
Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries) -
Question
Cut the given shape into three congruent parts:
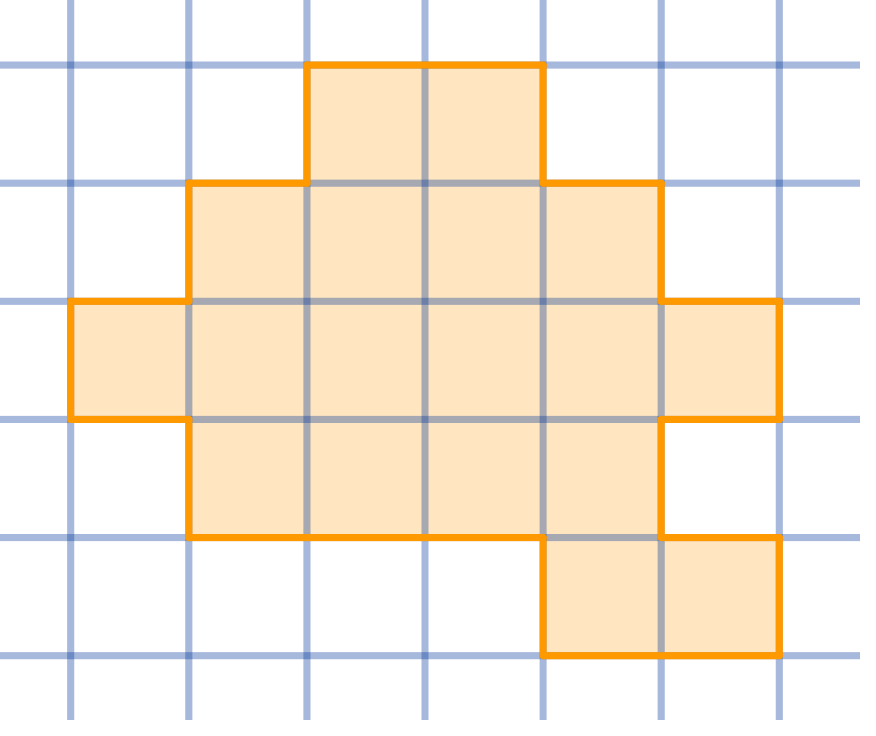 Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries)
Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries) -
Question
Divide the given shape into three congruent parts:
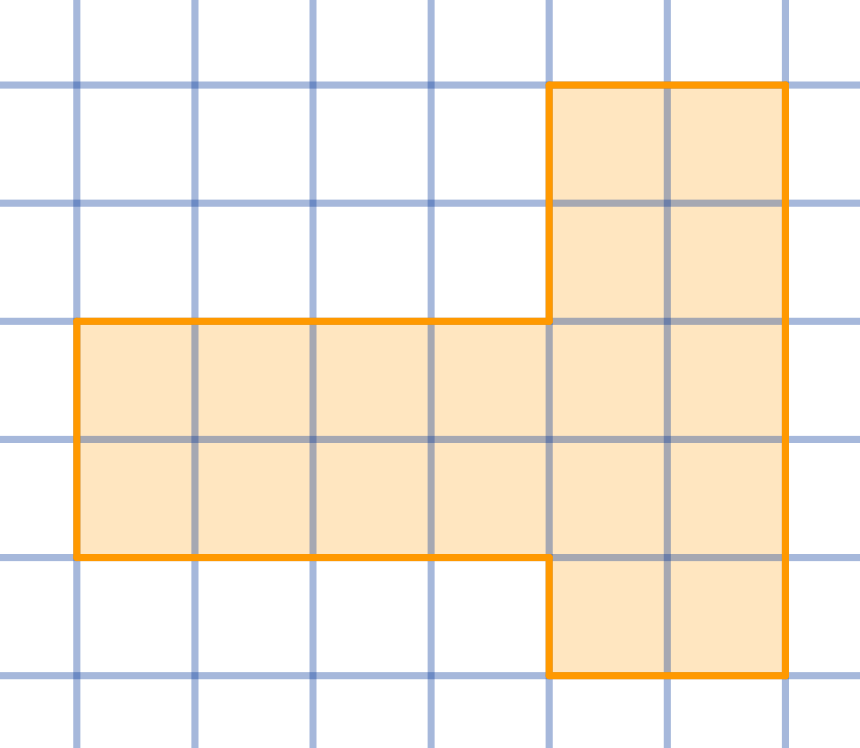 Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries)
Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries) -
Question
Partition the given shape into four congruent parts:
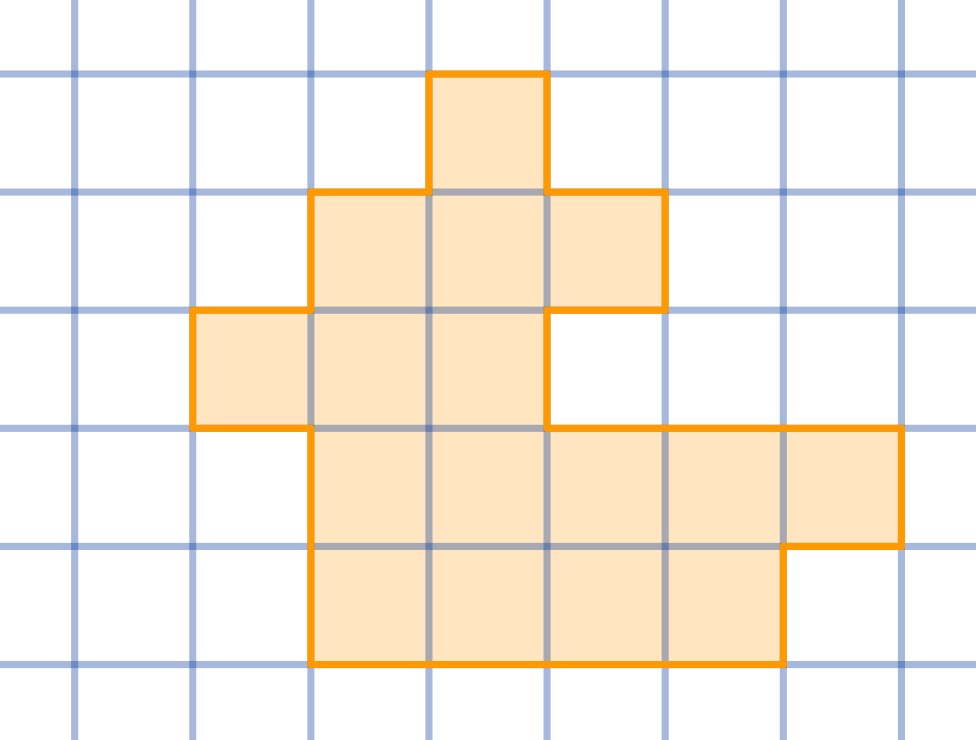 Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries) -> Reflection
Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries) -> Reflection