Geometry, Plane Geometry
Plane Geometry concerns figures and shapes on a flat, two-dimensional surface. It covers properties of points, lines, angles, polygons (like triangles and quadrilaterals), and circles. Questions typically involve proofs, constructions, and calculations related to these elements.
Area Calculation Triangles Circles Symmetry Angle Calculation Pythagorean Theorem Triangle Inequality-
THE BUN PUZZLE
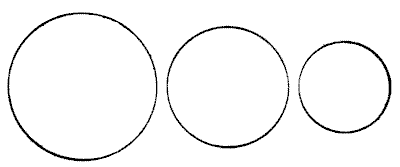 The three circles represent three buns, and it is simply required to show how these may be equally divided among four boys. The buns must be regarded as of equal thickness throughout and of equal thickness to each other. Of course, they must be cut into as few pieces as possible. To simplify it I will state the rather surprising fact that only five pieces are necessary, from which it will be seen that one boy gets his share in two pieces and the other three receive theirs in a single piece. I am aware that this statement "gives away" the puzzle, but it should not destroy its interest to those who like to discover the "reason why."
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Circles Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Pythagorean Theorem Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems
The three circles represent three buns, and it is simply required to show how these may be equally divided among four boys. The buns must be regarded as of equal thickness throughout and of equal thickness to each other. Of course, they must be cut into as few pieces as possible. To simplify it I will state the rather surprising fact that only five pieces are necessary, from which it will be seen that one boy gets his share in two pieces and the other three receive theirs in a single piece. I am aware that this statement "gives away" the puzzle, but it should not destroy its interest to those who like to discover the "reason why."
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Circles Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Pythagorean Theorem Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 148
-
THE GREAT MONAD

Here is a symbol of tremendous antiquity which is worthy of notice. It is borne on the Korean ensign and merchant flag, and has been adopted as a trade sign by the Northern Pacific Railroad Company, though probably few are aware that it is the Great Monad, as shown in the sketch below. This sign is to the Chinaman what the cross is to the Christian. It is the sign of Deity and eternity, while the two parts into which the circle is divided are called the Yin and the Yan—the male and female forces of nature. A writer on the subject more than three thousand years ago is reported to have said in reference to it: "The illimitable produces the great extreme. The great extreme produces the two principles. The two principles produce the four quarters, and from the four quarters we develop the quadrature of the eight diagrams of Feuh-hi." I hope readers will not ask me to explain this, for I have not the slightest idea what it means. Yet I am persuaded that for ages the symbol has had occult and probably mathematical meanings for the esoteric student.
I will introduce the Monad in its elementary form. Here are three easy questions respecting this great symbol:—
(I.) Which has the greater area, the inner circle containing the Yin and the Yan, or the outer ring?
(II.) Divide the Yin and the Yan into four pieces of the same size and shape by one cut.
(III.) Divide the Yin and the Yan into four pieces of the same size, but different shape, by one straight cut.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Circles Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 158
-
THE TWO HORSESHOES
Why horseshoes should be considered "lucky" is one of those things which no man can understand. It is a very old superstition, and John Aubrey (`1626-1700`) says, "Most houses at the West End of London have a horseshoe on the threshold." In Monmouth Street there were seventeen in `1813` and seven so late as `1855`. Even Lord Nelson had one nailed to the mast of the ship Victory. To-day we find it more conducive to "good luck" to see that they are securely nailed on the feet of the horse we are about to drive.
Nevertheless, so far as the horseshoe, like the Swastika and other emblems that I have had occasion at times to deal with, has served to symbolize health, prosperity, and goodwill towards men, we may well treat it with a certain amount of respectful interest. May there not, moreover, be some esoteric or lost mathematical mystery concealed in the form of a horseshoe? I have been looking into this matter, and I wish to draw my readers' attention to the very remarkable fact that the pair of horseshoes shown in my illustration are related in a striking and beautiful manner to the circle, which is the symbol of eternity. I present this fact in the form of a simple problem, so that it may be seen how subtly this relation has been concealed for ages and ages. My readers will, I know, be pleased when they find the key to the mystery.
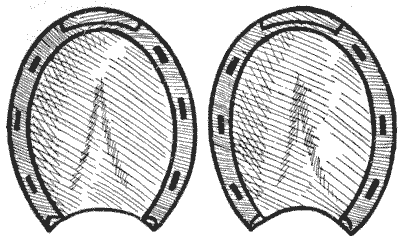
Cut out the two horseshoes carefully round the outline and then cut them into four pieces, all different in shape, that will fit together and form a perfect circle. Each shoe must be cut into two pieces and all the part of the horse's hoof contained within the outline is to be used and regarded as part of the area.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Circles Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 160
-
THE WIZARD'S CATS
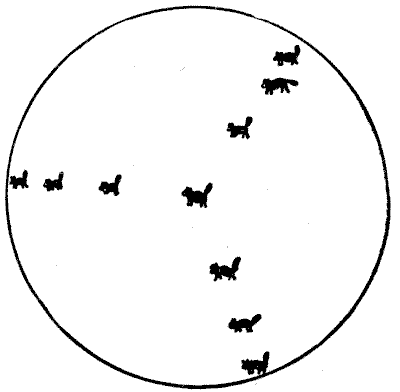 A wizard placed ten cats inside a magic circle as shown in our illustration, and hypnotized them so that they should remain stationary during his pleasure. He then proposed to draw three circles inside the large one, so that no cat could approach another cat without crossing a magic circle. Try to draw the three circles so that every cat has its own enclosure and cannot reach another cat without crossing a line.
Sources:
A wizard placed ten cats inside a magic circle as shown in our illustration, and hypnotized them so that they should remain stationary during his pleasure. He then proposed to draw three circles inside the large one, so that no cat could approach another cat without crossing a magic circle. Try to draw the three circles so that every cat has its own enclosure and cannot reach another cat without crossing a line.
Sources:
- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 167
-
THE GARDEN PUZZLE
Professor Rackbrain tells me that he was recently smoking a friendly pipe under a tree in the garden of a country acquaintance. The garden was enclosed by four straight walls, and his friend informed him that he had measured these and found the lengths to be `80, 45, 100`, and `63` yards respectively. "Then," said the professor, "we can calculate the exact area of the garden." "Impossible," his host replied, "because you can get an infinite number of different shapes with those four sides." "But you forget," Rackbrane said, with a twinkle in his eye, "that you told me once you had planted this tree equidistant from all the four corners of the garden." Can you work out the garden's area?Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Circles Algebra -> Equations Algebra -> Word Problems- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 182
-
DRAWING A SPIRAL
If you hold the page horizontally and give it a quick rotary motion while looking at the centre of the spiral, it will appear to revolve. Perhaps a good many readers are acquainted with this little optical illusion. But the puzzle is to show how I was able to draw this spiral with so much exactitude without using anything but a pair of compasses and the sheet of paper on which the diagram was made. How would you proceed in such circumstances?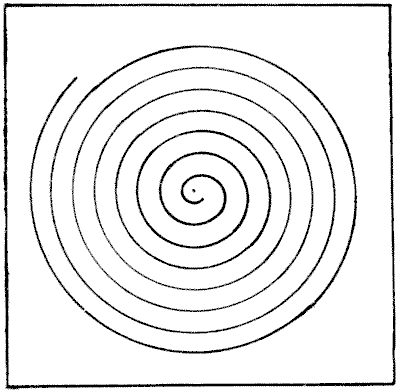 Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Circles
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Circles- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 183
-
THE CRESCENT PUZZLE
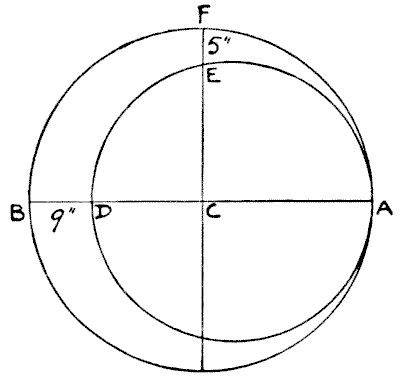 Here is an easy geometrical puzzle. The crescent is formed by two circles, and C is the centre of the larger circle. The width of the crescent between B and D is `9` inches, and between E and F `5` inches. What are the diameters of the two circles?
Sources:
Here is an easy geometrical puzzle. The crescent is formed by two circles, and C is the centre of the larger circle. The width of the crescent between B and D is `9` inches, and between E and F `5` inches. What are the diameters of the two circles?
Sources:
- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 191
-
THE GARDEN WALLS
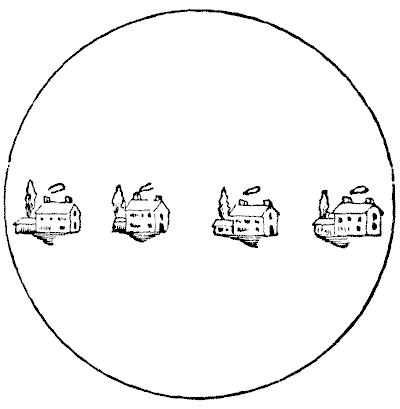
A speculative country builder has a circular field, on which he has erected four cottages, as shown in the illustration. The field is surrounded by a brick wall, and the owner undertook to put up three other brick walls, so that the neighbours should not be overlooked by each other, but the four tenants insist that there shall be no favouritism, and that each shall have exactly the same length of wall space for his wall fruit trees. The puzzle is to show how the three walls may be built so that each tenant shall have the same area of ground, and precisely the same length of wall.
Of course, each garden must be entirely enclosed by its walls, and it must be possible to prove that each garden has exactly the same length of wall. If the puzzle is properly solved no figures are necessary.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Circles Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 194
-
THE COMPASSES PUZZLE
It is curious how an added condition or restriction will sometimes convert an absurdly easy puzzle into an interesting and perhaps difficult one. I remember buying in the street many years ago a little mechanical puzzle that had a tremendous sale at the time. It consisted of a medal with holes in it, and the puzzle was to work a ring with a gap in it from hole to hole until it was finally detached. As I was walking along the street I very soon acquired the trick of taking off the ring with one hand while holding the puzzle in my pocket. A friend to whom I showed the little feat set about accomplishing it himself, and when I met him some days afterwards he exhibited his proficiency in the art. But he was a little taken aback when I then took the puzzle from him and, while simply holding the medal between the finger and thumb of one hand, by a series of little shakes and jerks caused the ring, without my even touching it, to fall off upon the floor. The following little poser will probably prove a rather tough nut for a great many readers, simply on account of the restricted conditions:—
Show how to find exactly the middle of any straight line by means of the compasses only. You are not allowed to use any ruler, pencil, or other article—only the compasses; and no trick or dodge, such as folding the paper, will be permitted. You must simply use the compasses in the ordinary legitimate way.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Circles- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 197
-
CONCERNING WHEELS
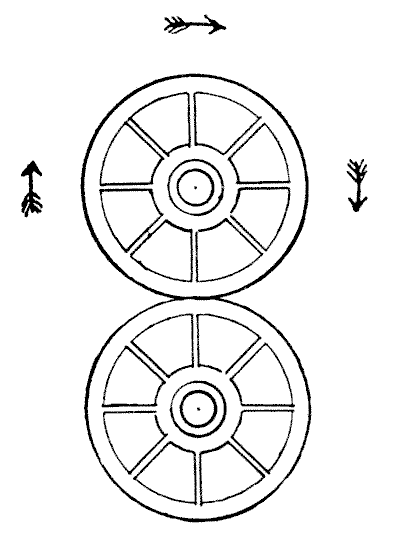
There are some curious facts concerning the movements of wheels that are apt to perplex the novice. For example: when a railway train is travelling from London to Crewe certain parts of the train at any given moment are actually moving from Crewe towards London. Can you indicate those parts? It seems absurd that parts of the same train can at any time travel in opposite directions, but such is the case.
In the accompanying illustration we have two wheels. The lower one is supposed to be fixed and the upper one running round it in the direction of the arrows. Now, how many times does the upper wheel turn on its own axis in making a complete revolution of the other wheel? Do not be in a hurry with your answer, or you are almost certain to be wrong. Experiment with two pennies on the table and the correct answer will surprise you, when you succeed in seeing it.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Circles Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries) -> Rotation- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 203