Geometry, Plane Geometry
Plane Geometry concerns figures and shapes on a flat, two-dimensional surface. It covers properties of points, lines, angles, polygons (like triangles and quadrilaterals), and circles. Questions typically involve proofs, constructions, and calculations related to these elements.
Area Calculation Triangles Circles Symmetry Angle Calculation Pythagorean Theorem Triangle Inequality-
PLACING HALFPENNIES
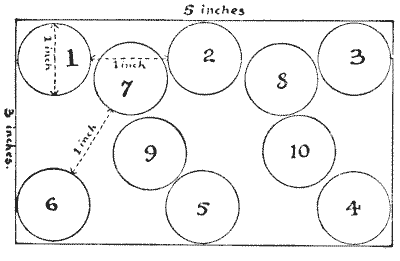 Here is an interesting little puzzle suggested to me by Mr. W. T. Whyte. Mark off on a sheet of paper a rectangular space `5` inches by `3` inches, and then find the greatest number of halfpennies that can be placed within the enclosure under the following conditions. A halfpenny is exactly an inch in diameter. Place your first halfpenny where you like, then place your second coin at exactly the distance of an inch from the first, the third an inch distance from the second, and so on. No halfpenny may touch another halfpenny or cross the boundary. Our illustration will make the matter perfectly clear. No. `2` coin is an inch from No. `1`; No. `3` an inch from No. `2`; No. `4` an inch from No. `3`; but after No. `10` is placed we can go no further in this attempt. Yet several more halfpennies might have been got in. How many can the reader place?
Sources:
Here is an interesting little puzzle suggested to me by Mr. W. T. Whyte. Mark off on a sheet of paper a rectangular space `5` inches by `3` inches, and then find the greatest number of halfpennies that can be placed within the enclosure under the following conditions. A halfpenny is exactly an inch in diameter. Place your first halfpenny where you like, then place your second coin at exactly the distance of an inch from the first, the third an inch distance from the second, and so on. No halfpenny may touch another halfpenny or cross the boundary. Our illustration will make the matter perfectly clear. No. `2` coin is an inch from No. `1`; No. `3` an inch from No. `2`; No. `4` an inch from No. `3`; but after No. `10` is placed we can go no further in this attempt. Yet several more halfpennies might have been got in. How many can the reader place?
Sources:
- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 429
-
Question
Given a line `l` and two points `A, B` at different distances from the line. Find the point `C` on the line such that the difference between the lengths of the segments `AC`, `AB` is maximal.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Triangle Inequality Minimum and Maximum Problems / Optimization Problems- Beno Arbel Olympiad, 2013, Grade 7 Question 3
-
Question
Let M be a set of points in the plane. O is called a partial center of symmetry if it is possible to remove a point from M such that O is a regular center of symmetry of what remains. How many partial centers of symmetry can a finite set of points in the plane have?
V. PrasolovSources:Topics:Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry Proof and Example -> Constructing an Example / Counterexample Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry- Tournament of Towns, 1980-1981, Spring, Main Version, Grades 9-10 Question 2 Points 7
-
Stack of Papers
Several identical rectangular sheets of paper lie on a table. It is known that the top sheet covers more than half the area of every other sheet. Is it necessarily possible to stick a pin into the table that will go through all these sheets?
Topics:Combinatorics -> Pigeonhole Principle Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry -
Question
Cut the given shape into two congruent parts:
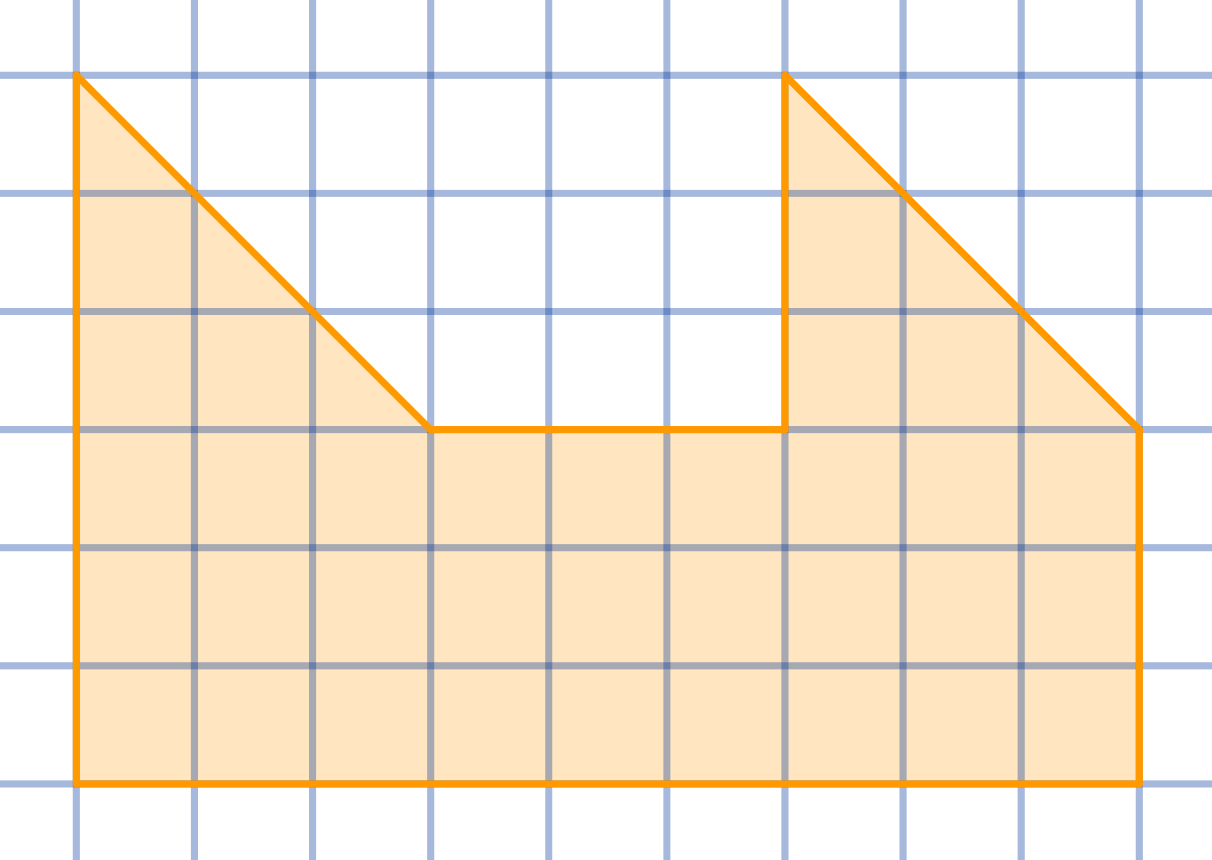 Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries)
Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries) -
Question
Cut the given shape into two congruent parts:
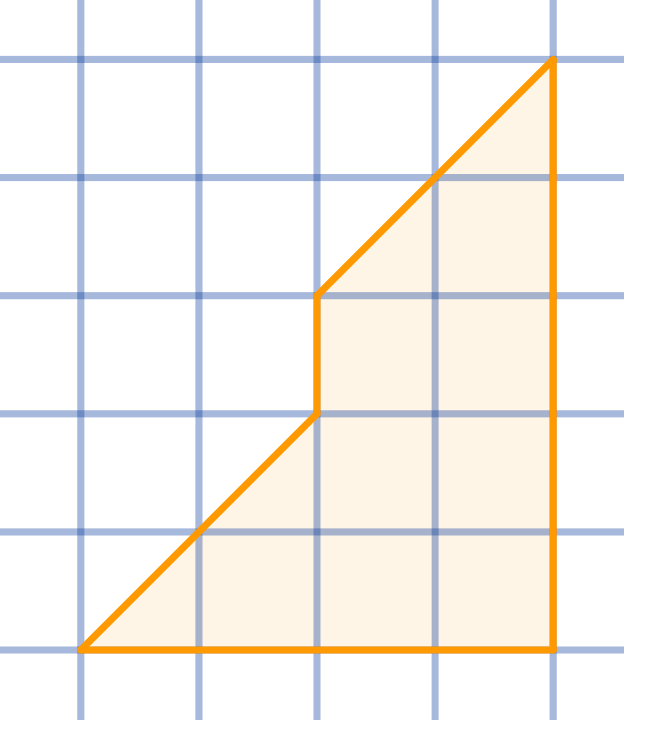 Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries)
Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries) -
Question
Cut the given shape into three congruent parts:
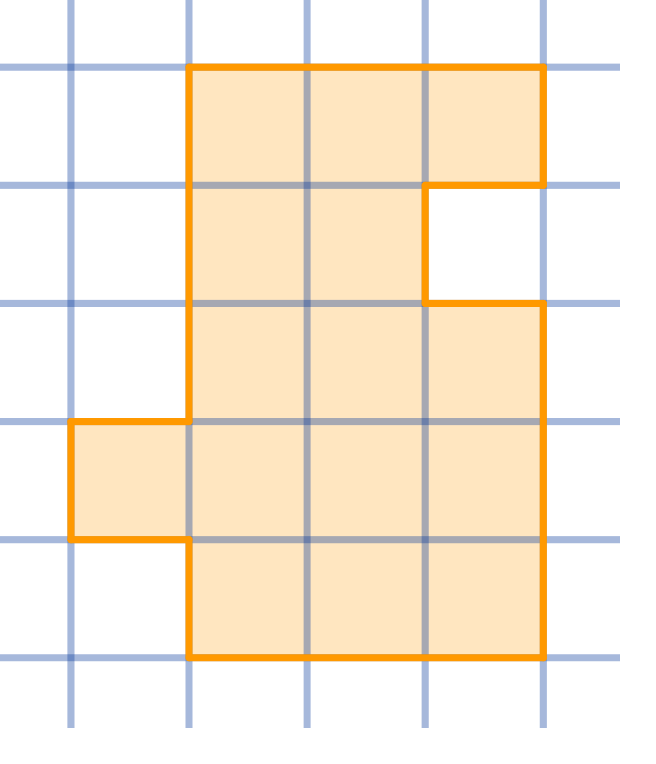 Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries)
Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries) -
Question
Cut the given shape into three congruent parts:
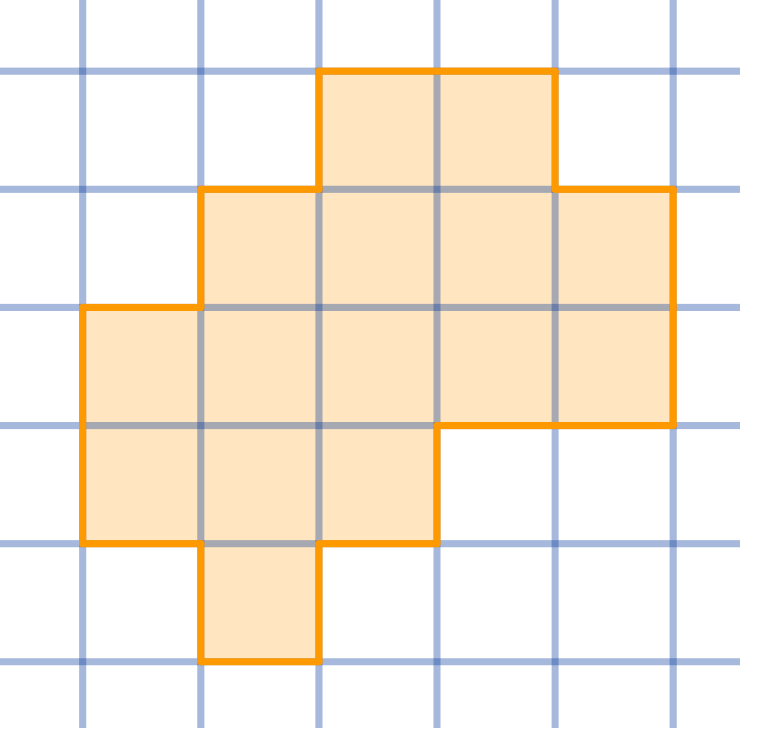 Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries)
Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries) -
Question
Cut the given shape into three congruent parts:
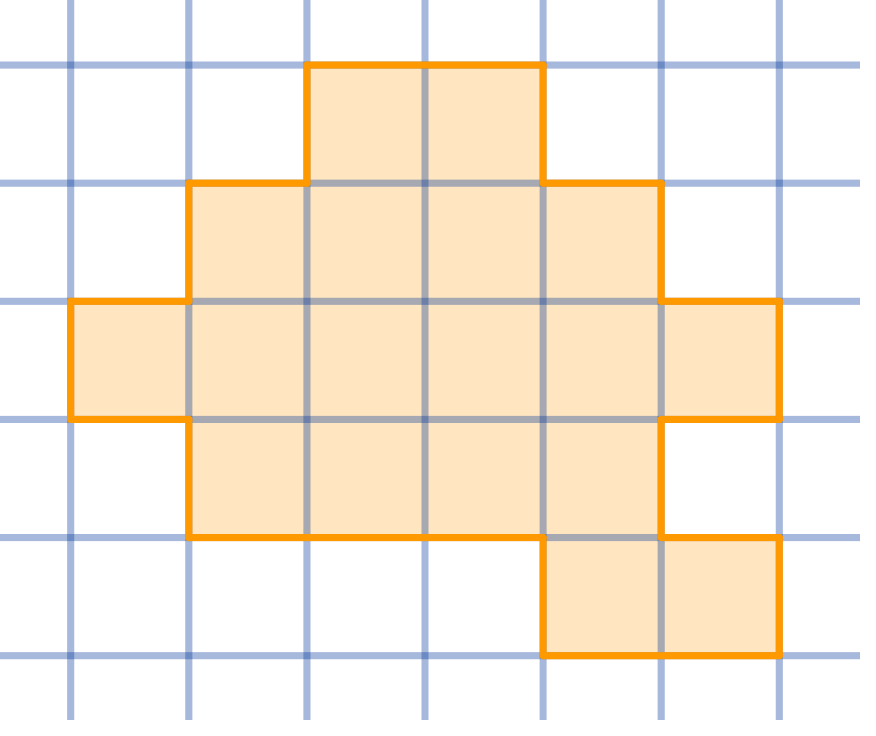 Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries)
Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries) -
Question
Divide the given shape into three congruent parts:
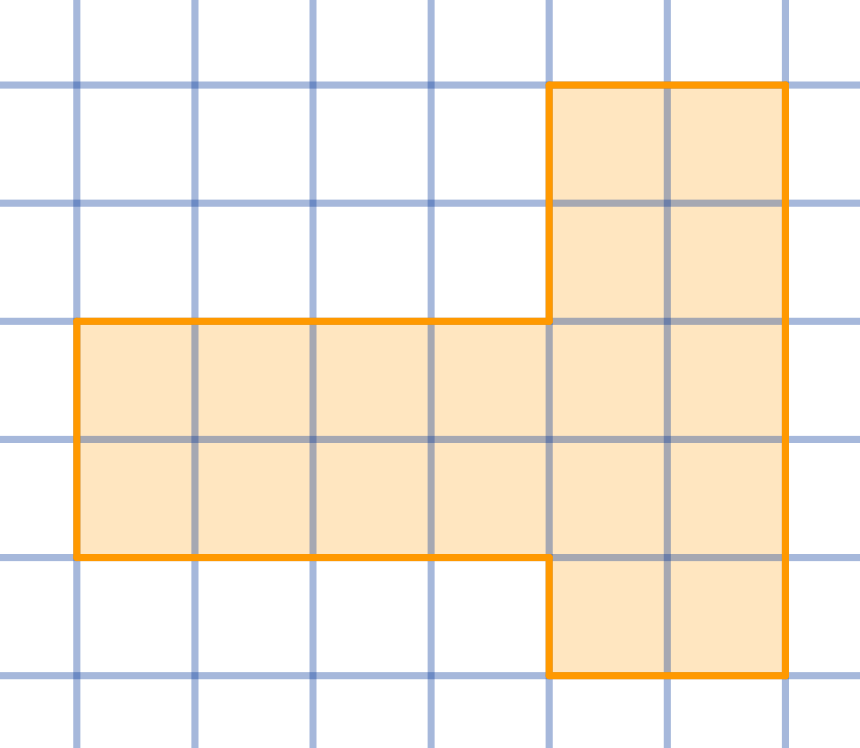 Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries)
Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries)