Geometry
Geometry is the branch of mathematics concerned with the properties and relations of points, lines, surfaces, solids, and higher dimensional analogues. Expected questions involve calculating lengths, angles, areas, and volumes of various shapes, understanding geometric theorems, and solving problems related to spatial reasoning.
Solid Geometry / Geometry in Space Trigonometry Spherical Geometry Plane Geometry Vectors-
THE SPOT ON THE TABLE
A boy, recently home from school, wished to give his father an exhibition of his precocity. He pushed a large circular table into the corner of the room, as shown in the illustration, so that it touched both walls, and he then pointed to a spot of ink on the extreme edge.
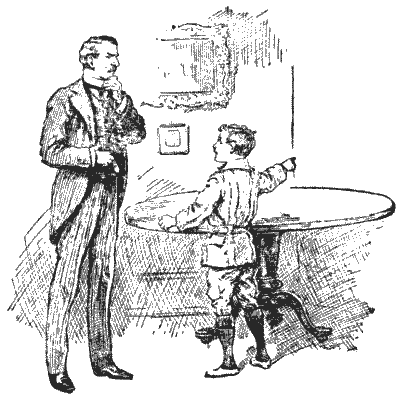
"Here is a little puzzle for you, pater," said the youth. "That spot is exactly eight inches from one wall and nine inches from the other. Can you tell me the diameter of the table without measuring it?"
The boy was overheard to tell a friend, "It fairly beat the guv'nor;" but his father is known to have remarked to a City acquaintance that he solved the thing in his head in a minute. I often wonder which spoke the truth.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Circles Algebra -> Equations Algebra -> Word Problems Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Pythagorean Theorem- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 97
-
REAPING THE CORN
A farmer had a square cornfield. The corn was all ripe for reaping, and, as he was short of men, it was arranged that he and his son should share the work between them. The farmer first cut one rod wide all round the square, thus leaving a smaller square of standing corn in the middle of the field. "Now," he said to his son, "I have cut my half of the field, and you can do your share." The son was not quite satisfied as to the proposed division of labour, and as the village schoolmaster happened to be passing, he appealed to that person to decide the matter. He found the farmer was quite correct, provided there was no dispute as to the size of the field, and on this point they were agreed. Can you tell the area of the field, as that ingenious schoolmaster succeeded in doing? Sources:- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 111
-
A FENCE PROBLEM
The practical usefulness of puzzles is a point that we are liable to overlook. Yet, as a matter of fact, I have from time to time received quite a large number of letters from individuals who have found that the mastering of some little principle upon which a puzzle was built has proved of considerable value to them in a most unexpected way. Indeed, it may be accepted as a good maxim that a puzzle is of little real value unless, as well as being amusing and perplexing, it conceals some instructive and possibly useful feature. It is, however, very curious how these little bits of acquired knowledge dovetail into the occasional requirements of everyday life, and equally curious to what strange and mysterious uses some of our readers seem to apply them. What, for example, can be the object of Mr. Wm. Oxley, who writes to me all the way from Iowa, in wishing to ascertain the dimensions of a field that he proposes to enclose, containing just as many acres as there shall be rails in the fence? The man wishes to fence in a perfectly square field which is to contain just as many acres as there are rails in the required fence. Each hurdle, or portion of fence, is seven rails high, and two lengths would extend one pole (`16`½ ft.): that is to say, there are fourteen rails to the pole, lineal measure. Now, what must be the size of the field?
Sources:
The man wishes to fence in a perfectly square field which is to contain just as many acres as there are rails in the required fence. Each hurdle, or portion of fence, is seven rails high, and two lengths would extend one pole (`16`½ ft.): that is to say, there are fourteen rails to the pole, lineal measure. Now, what must be the size of the field?
Sources:
- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 117
-
A QUESTION OF DEFINITION
"My property is exactly a mile square," said one landowner to another.
"Curiously enough, mine is a square mile," was the reply.
"Then there is no difference?"
Is this last statement correct?
Sources:- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 124
-
THE SCULPTOR'S PROBLEM
An ancient sculptor was commissioned to supply two statues, each on a cubical pedestal. It is with these pedestals that we are concerned. They were of unequal sizes, as will be seen in the illustration, and when the time arrived for payment a dispute arose as to whether the agreement was based on lineal or cubical measurement. But as soon as they came to measure the two pedestals the matter was at once settled, because, curiously enough, the number of lineal feet was exactly the same as the number of cubical feet. The puzzle is to find the dimensions for two pedestals having this peculiarity, in the smallest possible figures. You see, if the two pedestals, for example, measure respectively `3` ft. and `1` ft. on every side, then the lineal measurement would be `4` ft. and the cubical contents `28` ft., which are not the same, so these measurements will not do.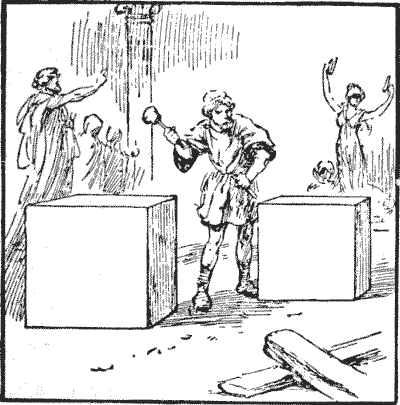 Sources:Topics:Number Theory Geometry -> Solid Geometry / Geometry in Space Arithmetic -> Fractions Algebra -> Equations -> Diophantine Equations
Sources:Topics:Number Theory Geometry -> Solid Geometry / Geometry in Space Arithmetic -> Fractions Algebra -> Equations -> Diophantine Equations- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 130
-
THE SILK PATCHWORK
The lady members of the Wilkinson family had made a simple patchwork quilt, as a small Christmas present, all composed of square pieces of the same size, as shown in the illustration. It only lacked the four corner pieces to make it complete. Somebody pointed out to them that if you unpicked the Greek cross in the middle and then cut the stitches along the dark joins, the four pieces all of the same size and shape would fit together and form a square. This the reader knows, from the solution in Fig. `39`, is quite easily done. But George Wilkinson suddenly suggested to them this poser. He said, "Instead of picking out the cross entire, and forming the square from four equal pieces, can you cut out a square entire and four equal pieces that will form a perfect Greek cross?" The puzzle is, of course, now quite easy.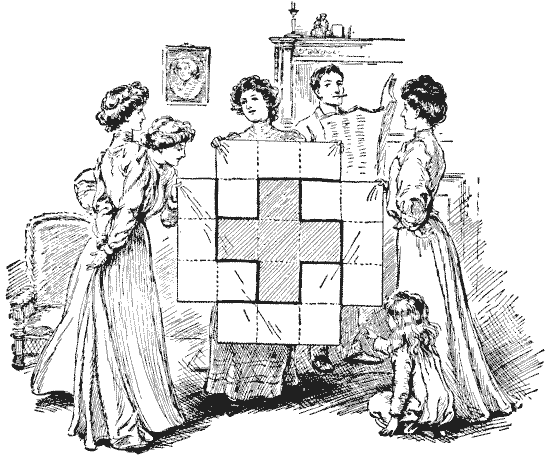 Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry Geometry -> Area Calculation Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry Geometry -> Area Calculation Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 142
-
TWO CROSSES FROM ONE
Cut a Greek cross into five pieces that will form two such crosses, both of the same size. The solution of this puzzle is very beautiful. Sources:- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 143
-
THE CROSS AND THE TRIANGLE
Cut a Greek cross into six pieces that will form an equilateral triangle. This is another hard problem, and I will state here that a solution is practically impossible without a previous knowledge of my method of transforming an equilateral triangle into a square (see No. `26`, "Canterbury Puzzles").Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Triangles Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 144
-
THE FOLDED CROSS
Cut out of paper a Greek cross; then so fold it that with a single straight cut of the scissors the four pieces produced will form a square.
Sources:- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 145
-
AN EASY DISSECTION PUZZLE
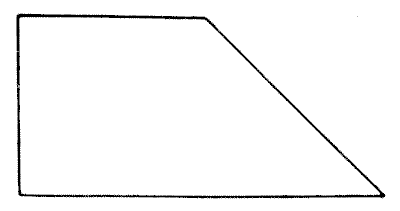
First, cut out a piece of paper or cardboard of the shape shown in the illustration. It will be seen at once that the proportions are simply those of a square attached to half of another similar square, divided diagonally. The puzzle is to cut it into four pieces all of precisely the same size and shape.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry Geometry -> Area Calculation Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 146