Geometry
Geometry is the branch of mathematics concerned with the properties and relations of points, lines, surfaces, solids, and higher dimensional analogues. Expected questions involve calculating lengths, angles, areas, and volumes of various shapes, understanding geometric theorems, and solving problems related to spatial reasoning.
Solid Geometry / Geometry in Space Trigonometry Spherical Geometry Plane Geometry Vectors-
AN EASY SQUARE PUZZLE
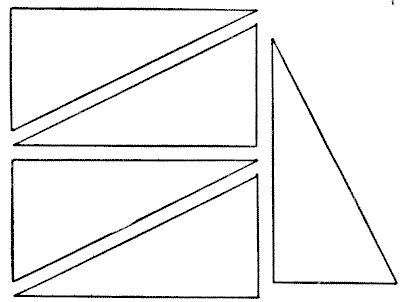
If you take a rectangular piece of cardboard, twice as long as it is broad, and cut it in half diagonally, you will get two of the pieces shown in the illustration. The puzzle is with five such pieces of equal size to form a square. One of the pieces may be cut in two, but the others must be used intact.
Sources:- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 147
-
THE BUN PUZZLE
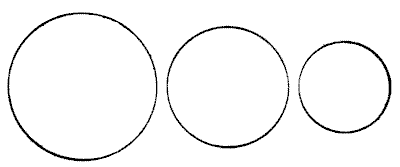 The three circles represent three buns, and it is simply required to show how these may be equally divided among four boys. The buns must be regarded as of equal thickness throughout and of equal thickness to each other. Of course, they must be cut into as few pieces as possible. To simplify it I will state the rather surprising fact that only five pieces are necessary, from which it will be seen that one boy gets his share in two pieces and the other three receive theirs in a single piece. I am aware that this statement "gives away" the puzzle, but it should not destroy its interest to those who like to discover the "reason why."
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Circles Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Pythagorean Theorem Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems
The three circles represent three buns, and it is simply required to show how these may be equally divided among four boys. The buns must be regarded as of equal thickness throughout and of equal thickness to each other. Of course, they must be cut into as few pieces as possible. To simplify it I will state the rather surprising fact that only five pieces are necessary, from which it will be seen that one boy gets his share in two pieces and the other three receive theirs in a single piece. I am aware that this statement "gives away" the puzzle, but it should not destroy its interest to those who like to discover the "reason why."
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Circles Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Pythagorean Theorem Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 148
-
THE CHOCOLATE SQUARES
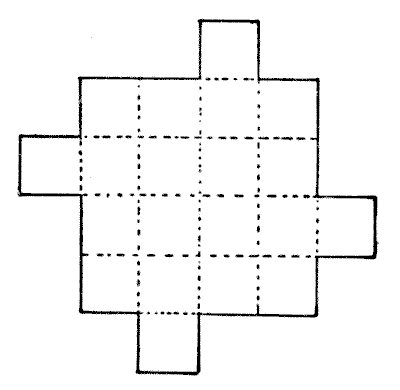 Here is a slab of chocolate, indented at the dotted lines so that the twenty squares can be easily separated. Make a copy of the slab in paper or cardboard and then try to cut it into nine pieces so that they will form four perfect squares all of exactly the same size.
Sources:
Here is a slab of chocolate, indented at the dotted lines so that the twenty squares can be easily separated. Make a copy of the slab in paper or cardboard and then try to cut it into nine pieces so that they will form four perfect squares all of exactly the same size.
Sources:
- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 149
-
DISSECTING A MITRE
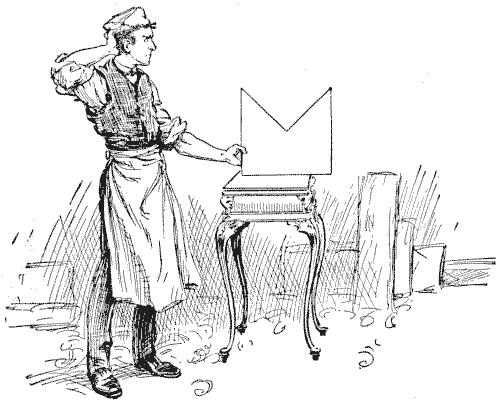
The figure that is perplexing the carpenter in the illustration represents a mitre. It will be seen that its proportions are those of a square with one quarter removed. The puzzle is to cut it into five pieces that will fit together and form a perfect square. I show an attempt, published in America, to perform the feat in four pieces, based on what is known as the "step principle," but it is a fallacy.
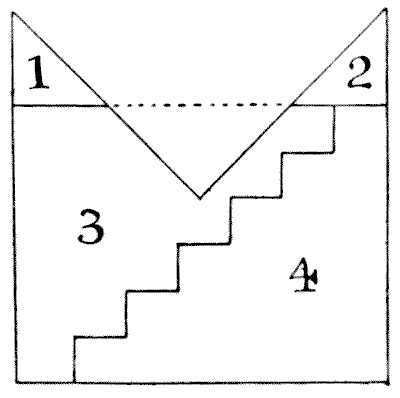
We are told first to cut oft the pieces `1` and `2` and pack them into the triangular space marked off by the dotted line, and so form a rectangle.
So far, so good. Now, we are directed to apply the old step principle, as shown, and, by moving down the piece `4` one step, form the required square. But, unfortunately, it does not produce a square: only an oblong. Call the three long sides of the mitre `84` in. each. Then, before cutting the steps, our rectangle in three pieces will be `84`×`63`. The steps must be `10`½ in. in height and `12` in. in breadth. Therefore, by moving down a step we reduce by `12` in. the side `84` in. and increase by `10`½ in. the side `63` in. Hence our final rectangle must be `72` in. × `73`½ in., which certainly is not a square! The fact is, the step principle can only be applied to rectangles with sides of particular relative lengths. For example, if the shorter side in this case were `61` `5/7` (instead of `63`), then the step method would apply. For the steps would then be `10` `2/7` in. in height and `12` in. in breadth. Note that `61` `5/7` × `84`= the square of `72`. At present no solution has been found in four pieces, and I do not believe one possible.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry Geometry -> Area Calculation Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 150
-
THE JOINER'S PROBLEM
I have often had occasion to remark on the practical utility of puzzles, arising out of an application to the ordinary affairs of life of the little tricks and "wrinkles" that we learn while solving recreation problems.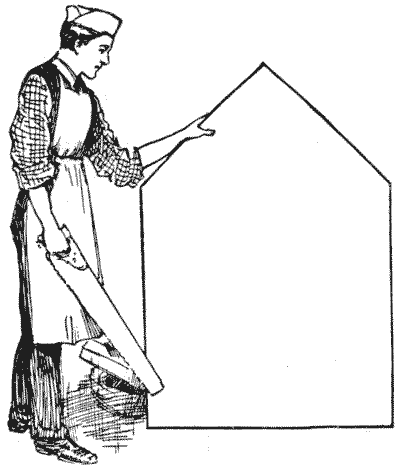 The joiner, in the illustration, wants to cut the piece of wood into as few pieces as possible to form a square table-top, without any waste of material. How should he go to work? How many pieces would you require?
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry Geometry -> Area Calculation Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems
The joiner, in the illustration, wants to cut the piece of wood into as few pieces as possible to form a square table-top, without any waste of material. How should he go to work? How many pieces would you require?
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry Geometry -> Area Calculation Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 151
-
ANOTHER JOINER'S PROBLEM
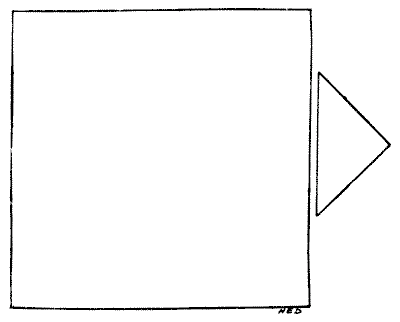 A joiner had two pieces of wood of the shapes and relative proportions shown in the diagram. He wished to cut them into as few pieces as possible so that they could be fitted together, without waste, to form a perfectly square table-top. How should he have done it? There is no necessity to give measurements, for if the smaller piece (which is half a square) be made a little too large or a little too small it will not affect the method of solution.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Pythagorean Theorem Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems
A joiner had two pieces of wood of the shapes and relative proportions shown in the diagram. He wished to cut them into as few pieces as possible so that they could be fitted together, without waste, to form a perfectly square table-top. How should he have done it? There is no necessity to give measurements, for if the smaller piece (which is half a square) be made a little too large or a little too small it will not affect the method of solution.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Pythagorean Theorem Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 152
-
A CUTTING-OUT PUZZLE
Here is a little cutting-out poser. I take a strip of paper, measuring five inches by one inch, and, by cutting it into five pieces, the parts fit together and form a square, as shown in the illustration. Now, it is quite an interesting puzzle to discover how we can do this in only four pieces.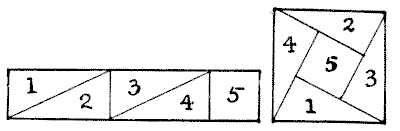 Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 153
-
MRS. HOBSON'S HEARTHRUG
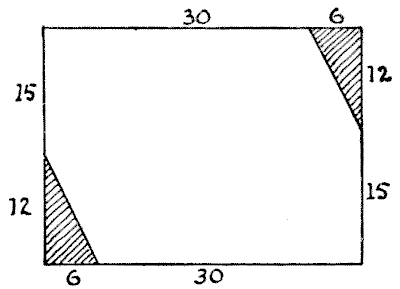
Mrs. Hobson's boy had an accident when playing with the fire, and burnt two of the corners of a pretty hearthrug. The damaged corners have been cut away, and it now has the appearance and proportions shown in my diagram. How is Mrs. Hobson to cut the rug into the fewest possible pieces that will fit together and form a perfectly square rug? It will be seen that the rug is in the proportions `36` × `27` (it does not matter whether we say inches or yards), and each piece cut away measured `12` and `6` on the outside.
Sources:- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 154
-
THE PENTAGON AND SQUARE
I wonder how many of my readers, amongst those who have not given any close attention to the elements of geometry, could draw a regular pentagon, or five-sided figure, if they suddenly required to do so. A regular hexagon, or six-sided figure, is easy enough, for everybody knows that all you have to do is to describe a circle and then, taking the radius as the length of one of the sides, mark off the six points round the circumference. But a pentagon is quite another matter. So, as my puzzle has to do with the cutting up of a regular pentagon, it will perhaps be well if I first show my less experienced readers how this figure is to be correctly drawn. Describe a circle and draw the two lines H B and D G, in the diagram, through the centre at right angles. Now find the point A, midway between C and B. Next place the point of your compasses at A and with the distance A D describe the arc cutting H B at E. Then place the point of your compasses at D and with the distance D E describe the arc cutting the circumference at F. Now, D F is one of the sides of your pentagon, and you have simply to mark off the other sides round the circle. Quite simple when you know how, but otherwise somewhat of a poser.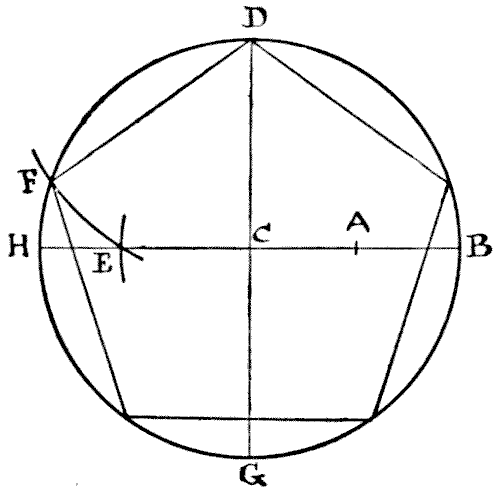 Having formed your pentagon, the puzzle is to cut it into the fewest possible pieces that will fit together and form a perfect square.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry Geometry -> Area Calculation Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Geometry -> Solid Geometry / Geometry in Space -> Polyhedra -> Regular Polyhedra
Having formed your pentagon, the puzzle is to cut it into the fewest possible pieces that will fit together and form a perfect square.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry Geometry -> Area Calculation Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Geometry -> Solid Geometry / Geometry in Space -> Polyhedra -> Regular Polyhedra- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 155
-
THE DISSECTED TRIANGLE
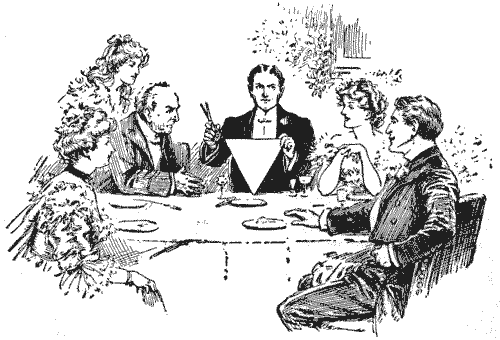
A good puzzle is that which the gentleman in the illustration is showing to his friends. He has simply cut out of paper an equilateral triangle—that is, a triangle with all its three sides of the same length. He proposes that it shall be cut into five pieces in such a way that they will fit together and form either two or three smaller equilateral triangles, using all the material in each case. Can you discover how the cuts should be made?
Remember that when you have made your five pieces, you must be able, as desired, to put them together to form either the single original triangle or to form two triangles or to form three triangles—all equilateral.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Triangles Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 156