Geometry
Geometry is the branch of mathematics concerned with the properties and relations of points, lines, surfaces, solids, and higher dimensional analogues. Expected questions involve calculating lengths, angles, areas, and volumes of various shapes, understanding geometric theorems, and solving problems related to spatial reasoning.
Solid Geometry / Geometry in Space Trigonometry Spherical Geometry Plane Geometry Vectors-
Inscribed Circle in a Triangle
Inside a triangle there is a point P, whose distances from the lines containing the sides of the triangle are `d_a,d_b,d_c`. Let R denote the radius of the circumscribed circle of the triangle and r the radius of the inscribed circle in the triangle. Show that `sqrt(d_a)+sqrt(d_b)+sqrt(d_3)<= sqrt (2R+5r) `.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Triangles Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Circles Algebra -> Inequalities- Gillis Mathematical Olympiad, 2019-2020 Question 7
-
Triangle Side Lengths
Let `n > 2` be an integer, and let ` t_1,t_2,...,t_n` be positive real numbers such that
`(t_1+t_2+...+t_n)(1/t_1 + 1/t_2 + ... + 1/t_n) < n^2+1`
Prove that for all i,j,k such that `1<=i<j<k<=n`, the triple of numbers `t_i,t_j,t_k` are the side lengths of a triangle.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Triangles Algebra -> Inequalities Proof and Example -> Proof by Contradiction Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Triangle Inequality- Grossman Math Olympiad, 2006 Question 5
-
Paths in a Triangular Park
In a park, there are 3 straight paths that form a triangle (there are no additional paths). The entrances to the park are at the midpoints of the paths, and a lamp hangs at each vertex of the triangle. From each entrance, the shortest walking distance along the park's paths to the lamp at the opposite vertex was measured. It turned out that 2 out of the 3 distances are equal to each other. Is the triangle necessarily isosceles?
 Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Triangles Proof and Example -> Constructing an Example / Counterexample Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Triangle Inequality
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Triangles Proof and Example -> Constructing an Example / Counterexample Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Triangle Inequality- Beno Arbel Olympiad, 2017, Grade 8 Question 3
-
THE THREE VILLAGES
I set out the other day to ride in a motor-car from Acrefield to Butterford, but by mistake I took the road going via Cheesebury, which is nearer Acrefield than Butterford, and is twelve miles to the left of the direct road I should have travelled. After arriving at Butterford I found that I had gone thirty-five miles. What are the three distances between these villages, each being a whole number of miles? I may mention that the three roads are quite straight.Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Triangles Algebra -> Word Problems Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Pythagorean Theorem- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 69
-
THE DISSECTED TRIANGLE
A good puzzle is that which the gentleman in the illustration is showing to his friends. He has simply cut out of paper an equilateral triangle—that is, a triangle with all its three sides of the same length. He proposes that it shall be cut into five pieces in such a way that they will fit together and form either two or three smaller equilateral triangles, using all the material in each case. Can you discover how the cuts should be made?
Remember that when you have made your five pieces, you must be able, as desired, to put them together to form either the single original triangle or to form two triangles or to form three triangles—all equilateral.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Triangles Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 156
-
PAPA'S PUZZLE
Here is a puzzle by Pappus, who lived at Alexandria about the end of the third century. It is the fifth proposition in the eighth book of his Mathematical Collections. I give it in the form that I presented it some years ago under the title "Papa's Puzzle," just to see how many readers would discover that it was by Pappus himself. "The little maid's papa has taken two different-sized rectangular pieces of cardboard, and has clipped off a triangular piece from one of them, so that when it is suspended by a thread from the point A it hangs with the long side perfectly horizontal, as shown in the illustration. He has perplexed the child by asking her to find the point A on the other card, so as to produce a similar result when cut and suspended by a thread." Of course, the point must not be found by trial clippings. A curious and pretty point is involved in this setting of the puzzle. Can the reader discover it?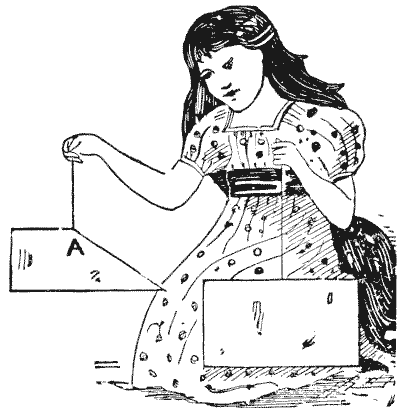 Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Triangles
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Triangles- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 199
-
Question
On a circle, `2016` blue points and one red point are marked. Consider all possible polygons whose vertices are at these points. Which polygons are more numerous – those that contain the red point or those whose vertices are all blue?
Sources: -
Question
`101` points are located on a circle. Which polygons with vertices at these points are more numerous – polygons with `51` sides or polygons with `50` sides?
-
Question
In a quadrilateral, the lengths of all diagonals and all sides are less than 1. Prove that the quadrilateral can be covered by a circle with a radius of 0.9.
Sources: -
Sets in the Plane
A. Does there exist a set A in the plane such that its intersection with every circle contains exactly two points?
B. Does there exist a set B in the plane such that its intersection with every circle of radius 1 contains exactly two points?
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Circles Proof and Example -> Constructing an Example / Counterexample Set Theory Proof and Example -> Proof by Contradiction Minimum and Maximum Problems / Optimization Problems- Grossman Math Olympiad, 2006 Question 3