Combinatorics
Combinatorics is the art of counting. It deals with selections, arrangements, and combinations of objects. Questions involve determining the number of ways to perform tasks, arrange items (permutations), or choose subsets (combinations), often using principles like the product rule and sum rule.
Pigeonhole Principle Double Counting Binomial Coefficients and Pascal's Triangle Product Rule / Rule of Product Graph Theory Matchings Induction (Mathematical Induction) Game Theory Combinatorial Geometry Invariants Case Analysis / Checking Cases Processes / Procedures Number Tables Colorings-
LINOLEUM CUTTING
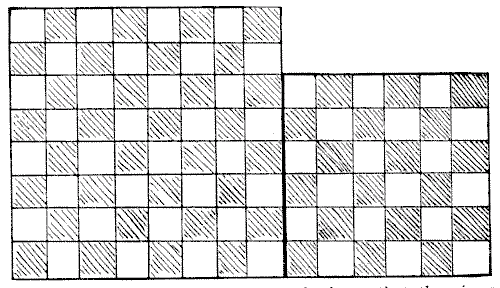 The diagram herewith represents two separate pieces of linoleum. The chequered pattern is not repeated at the back, so that the pieces cannot be turned over. The puzzle is to cut the two squares into four pieces so that they shall fit together and form one perfect square `10`×`10`, so that the pattern shall properly match, and so that the larger piece shall have as small a portion as possible cut from it.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Pythagorean Theorem Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems
The diagram herewith represents two separate pieces of linoleum. The chequered pattern is not repeated at the back, so that the pieces cannot be turned over. The puzzle is to cut the two squares into four pieces so that they shall fit together and form one perfect square `10`×`10`, so that the pattern shall properly match, and so that the larger piece shall have as small a portion as possible cut from it.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Pythagorean Theorem Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 176
-
ANOTHER LINOLEUM PUZZLE
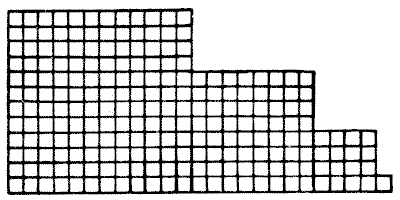
Can you cut this piece of linoleum into four pieces that will fit together and form a perfect square? Of course the cuts may only be made along the lines.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 177
-
THE FOUR SONS
Readers will recognize the diagram as a familiar friend of their youth. A man possessed a square-shaped estate. He bequeathed to his widow the quarter of it that is shaded off. The remainder was to be divided equitably amongst his four sons, so that each should receive land of exactly the same area and exactly similar in shape. We are shown how this was done. But the remainder of the story is not so generally known. In the centre of the estate was a well, indicated by the dark spot, and Benjamin, Charles, and David complained that the division was not "equitable," since Alfred had access to this well, while they could not reach it without trespassing on somebody else's land. The puzzle is to show how the estate is to be apportioned so that each son shall have land of the same shape and area, and each have access to the well without going off his own land.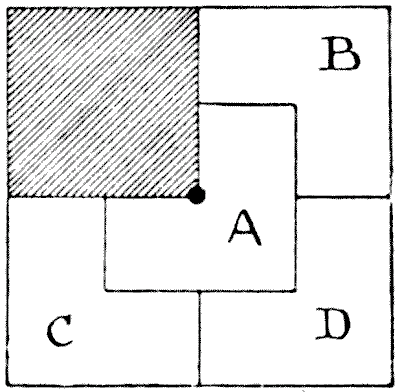 Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry Geometry -> Area Calculation Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry Geometry -> Area Calculation Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 180
-
THE GARDEN WALLS
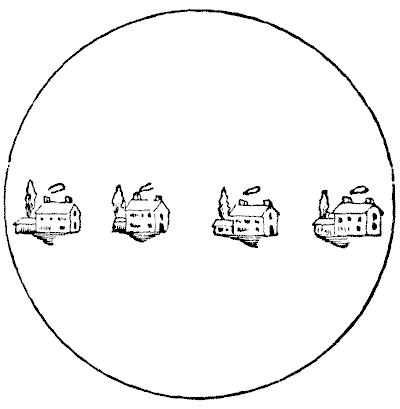
A speculative country builder has a circular field, on which he has erected four cottages, as shown in the illustration. The field is surrounded by a brick wall, and the owner undertook to put up three other brick walls, so that the neighbours should not be overlooked by each other, but the four tenants insist that there shall be no favouritism, and that each shall have exactly the same length of wall space for his wall fruit trees. The puzzle is to show how the three walls may be built so that each tenant shall have the same area of ground, and precisely the same length of wall.
Of course, each garden must be entirely enclosed by its walls, and it must be possible to prove that each garden has exactly the same length of wall. If the puzzle is properly solved no figures are necessary.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Circles Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 194
-
A NEW MATCH PUZZLE
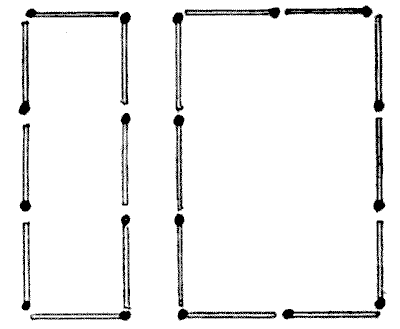 In the illustration eighteen matches are shown arranged so that they enclose two spaces, one just twice as large as the other. Can you rearrange them (`1`) so as to enclose two four-sided spaces, one exactly three times as large as the other, and (`2`) so as to enclose two five-sided spaces, one exactly three times as large as the other? All the eighteen matches must be fairly used in each case; the two spaces must be quite detached, and there must be no loose ends or duplicated matches.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Puzzles and Rebuses -> Matchstick Puzzles
In the illustration eighteen matches are shown arranged so that they enclose two spaces, one just twice as large as the other. Can you rearrange them (`1`) so as to enclose two four-sided spaces, one exactly three times as large as the other, and (`2`) so as to enclose two five-sided spaces, one exactly three times as large as the other? All the eighteen matches must be fairly used in each case; the two spaces must be quite detached, and there must be no loose ends or duplicated matches.
Sources:Topics:Geometry -> Area Calculation Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Puzzles and Rebuses -> Matchstick Puzzles- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 204
-
THE KING AND THE CASTLES
There was once, in ancient times, a powerful king, who had eccentric ideas on the subject of military architecture. He held that there was great strength and economy in symmetrical forms, and always cited the example of the bees, who construct their combs in perfect hexagonal cells, to prove that he had nature to support him. He resolved to build ten new castles in his country all to be connected by fortified walls, which should form five lines with four castles in every line. The royal architect presented his preliminary plan in the form I have shown. But the monarch pointed out that every castle could be approached from the outside, and commanded that the plan should be so modified that as many castles as possible should be free from attack from the outside, and could only be reached by crossing the fortified walls. The architect replied that he thought it impossible so to arrange them that even one castle, which the king proposed to use as a royal residence, could be so protected, but his majesty soon enlightened him by pointing out how it might be done. How would you have built the ten castles and fortifications so as best to fulfil the king's requirements? Remember that they must form five straight lines with four castles in every line.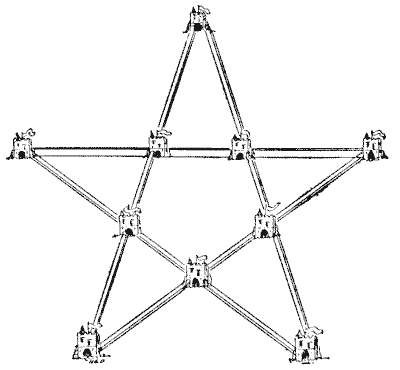 Sources:
Sources:
- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 206
-
CHERRIES AND PLUMS
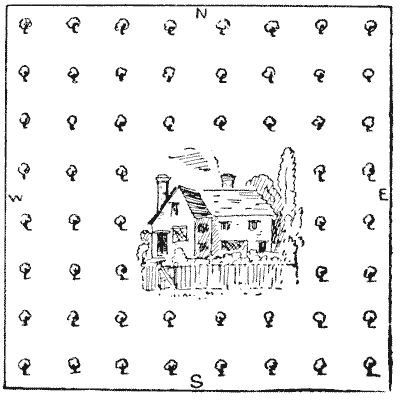 The illustration is a plan of a cottage as it stands surrounded by an orchard of fifty-five trees. Ten of these trees are cherries, ten are plums, and the remainder apples. The cherries are so planted as to form five straight lines, with four cherry trees in every line. The plum trees are also planted so as to form five straight lines with four plum trees in every line. The puzzle is to show which are the ten cherry trees and which are the ten plums. In order that the cherries and plums should have the most favourable aspect, as few as possible (under the conditions) are planted on the north and east sides of the orchard. Of course in picking out a group of ten trees (cherry or plum, as the case may be) you ignore all intervening trees. That is to say, four trees may be in a straight line irrespective of other trees (or the house) being in between. After the last puzzle this will be quite easy.
Sources:
The illustration is a plan of a cottage as it stands surrounded by an orchard of fifty-five trees. Ten of these trees are cherries, ten are plums, and the remainder apples. The cherries are so planted as to form five straight lines, with four cherry trees in every line. The plum trees are also planted so as to form five straight lines with four plum trees in every line. The puzzle is to show which are the ten cherry trees and which are the ten plums. In order that the cherries and plums should have the most favourable aspect, as few as possible (under the conditions) are planted on the north and east sides of the orchard. Of course in picking out a group of ten trees (cherry or plum, as the case may be) you ignore all intervening trees. That is to say, four trees may be in a straight line irrespective of other trees (or the house) being in between. After the last puzzle this will be quite easy.
Sources:
- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 207
-
A PLANTATION PUZZLE
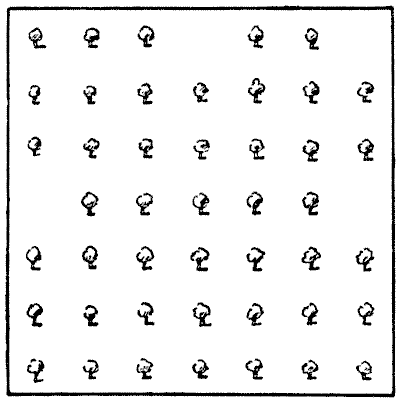 A man had a square plantation of forty-nine trees, but, as will be seen by the omissions in the illustration, four trees were blown down and removed. He now wants to cut down all the remainder except ten trees, which are to be so left that they shall form five straight rows with four trees in every row. Which are the ten trees that he must leave?
Sources:
A man had a square plantation of forty-nine trees, but, as will be seen by the omissions in the illustration, four trees were blown down and removed. He now wants to cut down all the remainder except ten trees, which are to be so left that they shall form five straight rows with four trees in every row. Which are the ten trees that he must leave?
Sources:
- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 208
-
THE TWENTY-ONE TREES
A gentleman wished to plant twenty-one trees in his park so that they should form twelve straight rows with five trees in every row. Could you have supplied him with a pretty symmetrical arrangement that would satisfy these conditions? Sources:- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 209
-
THE TEN COINS
Place ten pennies on a large sheet of paper or cardboard, as shown in the diagram, five on each edge. Now remove four of the coins, without disturbing the others, and replace them on the paper so that the ten shall form five straight lines with four coins in every line. This in itself is not difficult, but you should try to discover in how many different ways the puzzle may be solved, assuming that in every case the two rows at starting are exactly the same.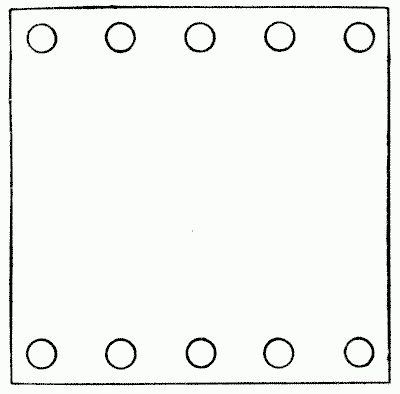 Sources:
Sources:
- Amusements in Mathematics, Henry Ernest Dudeney Question 210