Combinatorics
Combinatorics is the art of counting. It deals with selections, arrangements, and combinations of objects. Questions involve determining the number of ways to perform tasks, arrange items (permutations), or choose subsets (combinations), often using principles like the product rule and sum rule.
Pigeonhole Principle Double Counting Binomial Coefficients and Pascal's Triangle Product Rule / Rule of Product Graph Theory Matchings Induction (Mathematical Induction) Game Theory Combinatorial Geometry Invariants Case Analysis / Checking Cases Processes / Procedures Number Tables Colorings-
Question
Can the product of two consecutive natural numbers be equal to the product of two consecutive even numbers?
-
Question
`10` identical books cost more than `11` dollars, and `9` books of the same type cost less than `10` dollars. How much does one book cost?
Topics:Algebra -> Inequalities Algebra -> Word Problems Combinatorics -> Case Analysis / Checking Cases -> Processes / Procedures -
Stack of Papers
Several identical rectangular sheets of paper lie on a table. It is known that the top sheet covers more than half the area of every other sheet. Is it necessarily possible to stick a pin into the table that will go through all these sheets?
Topics:Combinatorics -> Pigeonhole Principle Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry Geometry -> Area Calculation Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry -
Question
The magical land consists of `25` provinces. Is it possible that each province borders an odd number of other provinces?
-
Question
Prove that there is no polyhedron with `7` edges.
-
Question
A number of lines and circles are drawn in the plane. Prove that it is possible to color the regions into which the plane is divided using two colors such that neighboring regions (those sharing a line segment or arc) are colored with different colors.
-
Question
Prove that every polyhedron has at least two faces with the same number of edges.
-
Question
A `29×29` table contains all integers from `1` to `29`, each appearing exactly `29` times. The sum of all numbers above the main diagonal is exactly three times greater than the sum of all numbers below the main diagonal. What number is written in the central cell of the table?
-
Question
From a chessboard, two opposite corners are removed (the squares `a1` and `h8`, for example). Can you tile the remaining board with dominoes?
-
Question
Cut the given shape into two congruent parts:
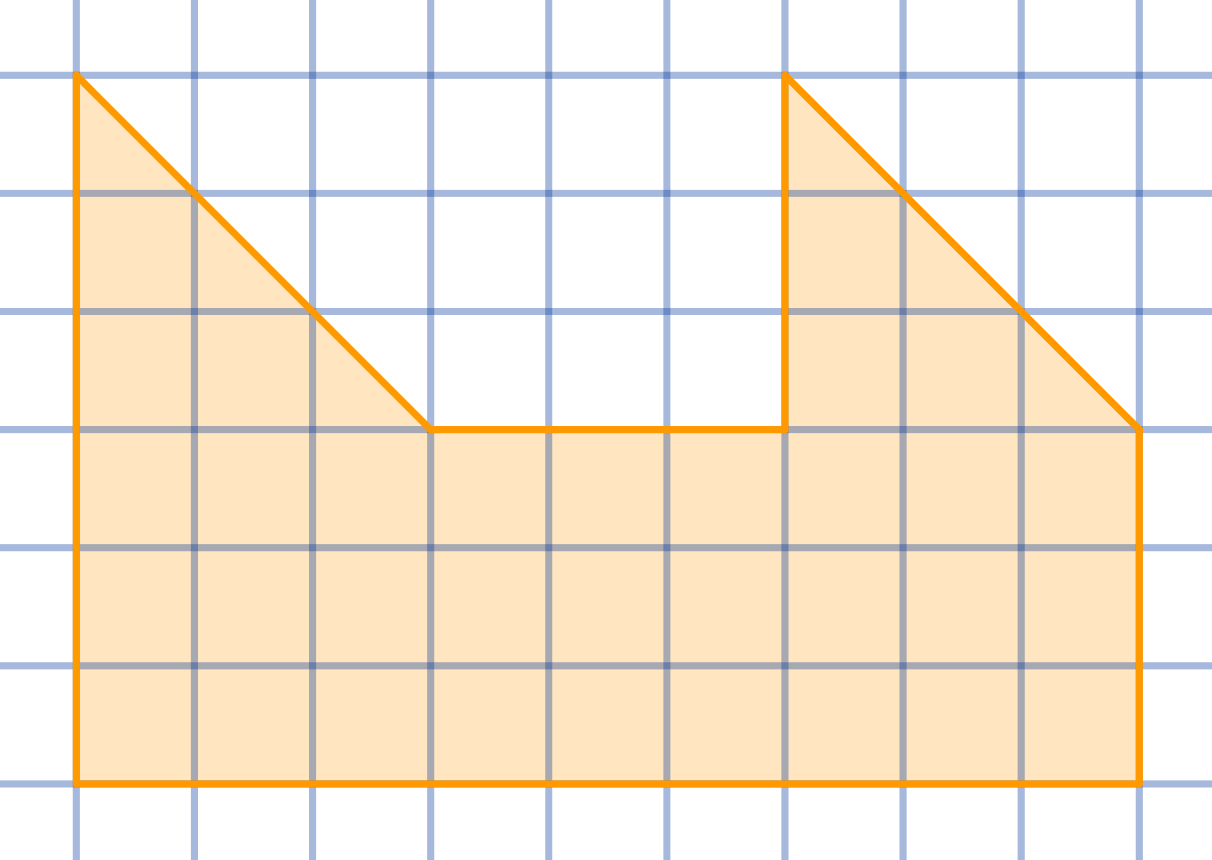 Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries)
Topics:Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Symmetry Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Cut a Shape / Dissection Problems Combinatorics -> Combinatorial Geometry -> Grid Paper Geometry / Lattice Geometry Geometry -> Plane Geometry -> Plane Transformations -> Congruence Transformations (Isometries)